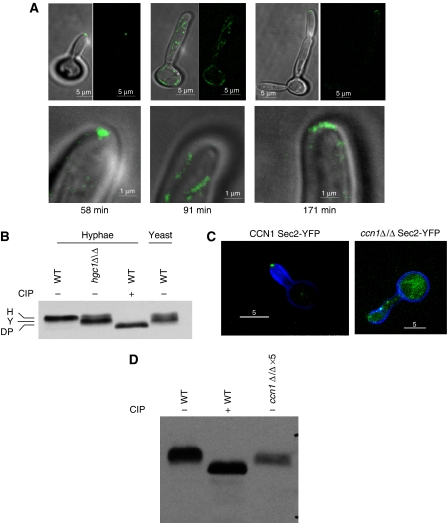
Figure 6.
Cells lacking Hgc1 are unable to maintain hyphal growth and show the yeast pattern of phosphorylation. (A) Frames from a timelapse video of an hgcΔ/Δ Sec2-YFP cell induced to form hyphae showing morphology and localization of Sec2-YFP. Times refer to minutes after stationary phase cells were re-inoculated into hyphal-inducing conditions. Top row merged DIC and fluorescent images (left) and fluorescent images alone (right). Bottom row shows detail of the tip of the same cells shown in the top row. Ten other timelapse videos gave similar results. Scale bars: top row, 5 μm; bottom row, 1 μm. (B) Sec2-YFP shows the yeast pattern of phosphorylation in cells lacking Hgc1. Hyphal cells were grown for 90 min after induction of hyphal growth, yeast cells were grown for 120 min. (C) Sec2-YFP is delocalized and hyphal tips swollen in a cell lacking Ccn1. Images taken 60 min after induction of hyphae. (D) Sec2-YFP shows the yeast pattern of phosphorylation and is destabilized in cells lacking Ccn1. Protein content of cell lysates was determined with a Bradford assay. To visualize the Sec2 YFP signal from a ccn1Δ/Δ strain, it was necessary to increase the amount of cell lysate five-fold compared with the wild-type control and the signal was still weaker. Scale bars: 5 μm.