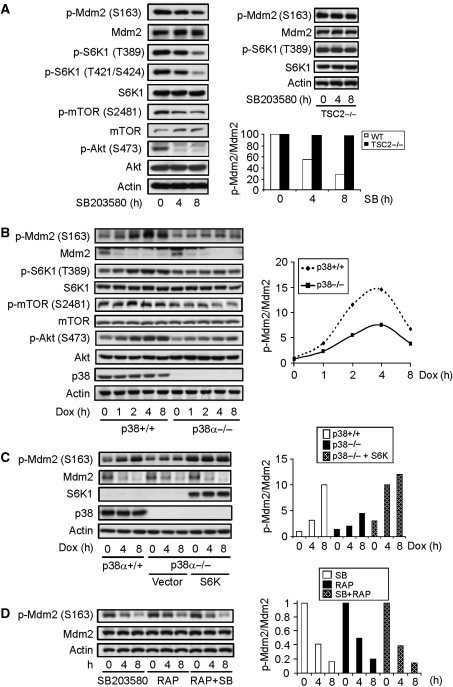
Figure 2.
Genotoxic stress activates p38α-mTOR-S6K pathway to phosphorylate Mdm2 on S163. (A) Inhibition of p38α with an inhibitor decreased Mdm2 S163 phosphorylation, S6K1 T389 phosphorylation, and mTOR S2481 phosphorylation in normal MEFs (left panel) but not in Tsc2−/− MEFs (right upper panel). Normal and Tsc2−/− MEFs were treated with p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 for different periods of time and Mdm2 phosphorylation and S6K1 activation were analysed with western blot. (Right bottom panel) Quantitation data of Mdm2 S163 phosphorylation normalized to Mdm2 protein levels. The value of p-Mdm2 S163 at time 0 in the presence of SB was set at 1.0. (B) p38α deficiency also resulted in decreased Mdm2 S163 phosphorylation and S6K1 T389 phosphorylation. (Right panel) Quantitation data of Mdm2 S163 phosphorylation normalized to Mdm2 protein levels. The value of p-Mdm2 S163 at time 0 in control WT MEFs was set at 1.0. (C) Ectopic expression of S6K rescued the Mdm2 S163 phosphorylation defect in p38α−/− MEFs. p38α-deficient MEFs infected with control retrovirus or virus expressing S6K1 were treated with Dox for different periods of time. Mdm2 S163 phosphorylation and Mdm2 were analysed with western blot. (Right panel) Quantitation data of Mdm2 S163 phosphorylation normalized to Mdm2 protein levels. The value of p-Mdm2 S163 at time 0 in control WT MEFs was set at 1.0. (D) Combinational use of rapamycin and SB203580 showed no additive effect on the suppression of Mdm2 S163 phosphorylation. MEFs were treated with p38 inhibitor, Rapamycin, or both for different periods of time. Mdm2 phosphorylation was analysed with western blot. (Right panel) Quantitation data of Mdm2 S163 phosphorylation normalized to Mdm2 protein levels. The value of p-Mdm2 S163 at time 0 in presence of SB was set at 1.0.