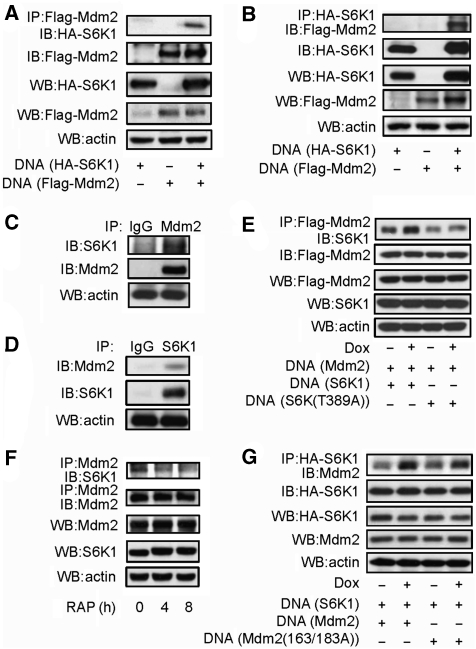
Figure 3.
Mdm2 interacts with S6K1. (A) Interaction between S6K1 and Mdm2. HA-S6K1, Flag-Mdm2, or both was expressed in 293T cells. Flag-Mdm2 was immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibodies and Mdm2-associated S6K1 was detected by western blot. (B) Same as Figure 3A, except that HA-S6K1 was immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibodies and S6K1-associated Mdm2 was detected by western blot. (C) Interaction of endogenous S6K and Mdm2 in MEFs. Endogenous Mdm2 was immunoprecipitated with antibodies against Mdm2 and Protein A plus G beads. Mdm2-associated S6K1 was detected by western blot. (D) Endogenous S6K1 was immunoprecipitated with antibodies against S6K1 and Protein A plus G beads. S6K1-associated Mdm2 was detected by western blot. (E) Genotoxic stress enhanced Mdm2–S6K1 interaction, which required T389 phosphorylation of S6K1. HA-S6K1 or HA-mutant S6K (T389A) together with Flag-Mdm2 was expressed in 293T cells. Transfected cells were treated with Dox for 2 h before preparation of cell lyse, then Flag-Mdm2 was immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibodies and Mdm2-associated S6K1 was detected by western blot. (F) Endogenous S6K1–Mdm2 interaction was disrupted by rapamycin. MEFs were treated with rapamycin for different periods of time, then endogenous Mdm2 was immunoprecipitated with antibodies against Mdm2 and Protein A plus G beads. Mdm2-associated S6K1 was detected by western blot. (G) Genotoxic stress-enhanced Mdm2–S6K1 interaction did not require S163/183 phosphorylation of Mdm2. HA-S6K1 together with Flag-Mdm2 or Flag-mutant Mdm2 (S163A/S183A) was expressed in 293T cells. Transfected cells were treated with Dox for 2 h before preparation of cell lyse, then HA-S6K1 was immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibodies and S6K1-associated Mdm2 was detected by western blot.