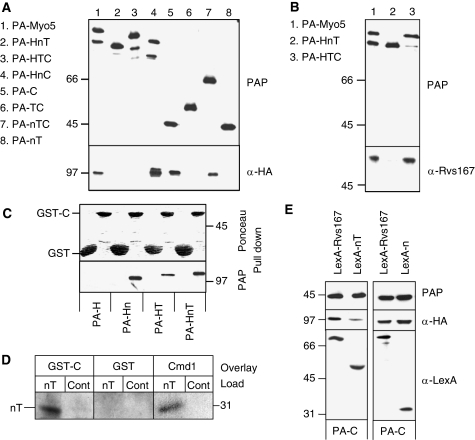
Figure 2.
The Myo5 TH1 domain blocks the interaction of the Myo5 Cext with Vrp1. (A, B, E) Immunoblots of IgG-Sepharose pull downs from myo5Δ vrp1Δ cells (SCMIG304), expressing the indicated PA-Myo5 constructs and Vrp1-HA, either overexpressing (E) or not (A, B) the indicated LexA fusion proteins (E). PAP, a peroxidase-conjugated anti-HA antibody and anti-Rvs167 or anti-Cmd1 antibodies, combined with the adequate peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody, were used for detection of the PA-Myo5 constructs, Vrp1-HA, Rvs167 and Cmd1, respectively. All PA-Myo5 constructs and Vrp1-HA were expressed from centromeric plasmids under the control of their own promoters. (C) Immunoblot of glutathione-Sepharose pull downs of GST-C or GST, incubated with extracts of a myo5Δ strain (SCMIG275), expressing the indicated PA-Myo5 constructs from centromeric plasmids under the MYO5 promoter, decorated with Ponceau red to detect GST-C and GST or PAP to detect the PA-Myo5 constructs. (D) Overlay assay of an Myo5 nT fragment, partially renatured after SDS–PAGE and western blot, incubated with 20 mM GST or GST fused to the Myo5 Cext (GST-C) or 60 mM Cmd1. GST and Cmd1 were detected using anti-GST and anti-Cmd1 antibodies and the adequate peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies. Control lanes (Cont) were loaded with residual proteins that might elute from the IgG-Sepharose under the conditions used for the nT purification, derived from a strain not expressing the PA-nT fragment.