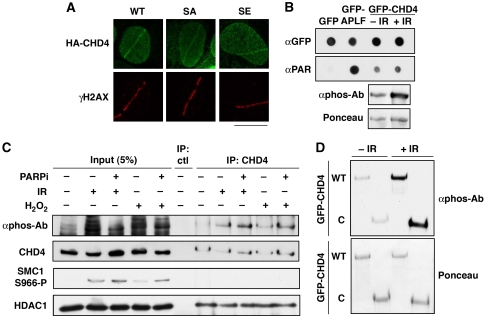
Figure 4.
DNA-damage-induced phosphorylation and recruitment of CHD4 to DNA lesions are distinct events. (A) Recruitment of HA-CHD4 wild-type (WT) and Ser-1346 point mutants (SA, mutated to Ala; SE, mutated to Glu) to sites of laser-induced damage (γH2AX) in transiently transfected U2OS cells 5 min after micro-irradiation. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) PAR-binding activity of GFP-CHD4 from HEK-293 cells exposed or not to ionizing radiation (IR). GFP only is used as a negative control, GFP-APLF as a positive control. Lower panel shows CHD4 phosphorylation after IR analysed in parallel by western blotting. (C) Detection of CHD4 phosphorylation (αphos-Ab) 30 min after exposure to 10 Gy ionizing radiation (IR) or 500 μM hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) on CHD4 immunoprecipitates from HEK-293 cells treated or not with PARP inhibitor (PARPi). SMC1 phosphorylation is used as a control for DNA damage. The NuRD subunit HDAC1 co-immunoprecipitates with CHD4. (D) Detection of CHD4 phosphorylation (αphos-Ab) 30 min after exposure to 10 Gy ionizing radiation (IR) on GFP immunoprecipitates from H3K293 cells transiently expressing GFP-CHD4 wild-type (WT) or a truncated mutant (C: residues 1183–1937).