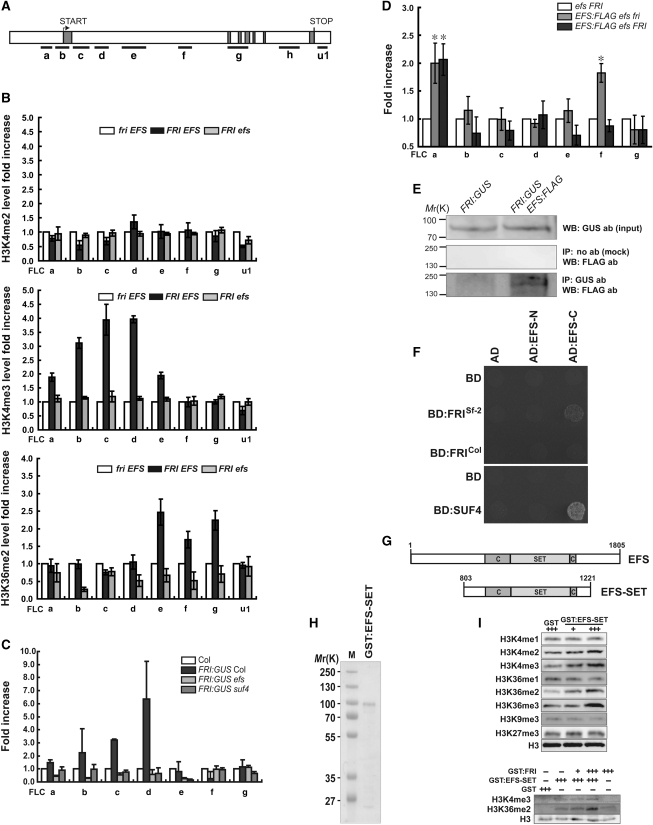
Figure 1.
FRI- and EFS-dependent H3K4 and H3K36 methylation of FLC chromatin. (A) FLC locus with exons (grey boxes) and introns (white boxes) showing regions tested for ChIP. (B) ChIP-quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) analyses of FLC chromatin with indicated histone antibodies (abs). fri EFS is wild-type Columbia (Col). Error bars represent s.e. (B–D). (C, D) ChIP-qPCR to test the direct association of FRI:GUS (C) or EFS:FLAG (D) with FLC chromatin using GUS (C) or FLAG (D) ab. (*P<0.05 versus control in a Student's t-test). (E) Co-IP of FRI:GUS and EFS:FLAG. Western blot (WB) was performed with the indicated abs. (F) Interaction of EFS with FRI and SUF4 in yeast two-hybrid assays. The N-terminal (EFS-N) or C-terminal region (EFS-C) of EFS were fused to the GAL4 activation domain (AD). FRI from Sf-2 or Col and SUF4 were fused to the GAL4-binding domain (BD). (G) Domains in EFS and EFS-SET. (H) Coomassie-stained purified GST:EFS-SET. (I) HMT activity of GST:EFS-SET in assays using calf thymus histones (upper) or oligonucleosomes (lower) as substrates.