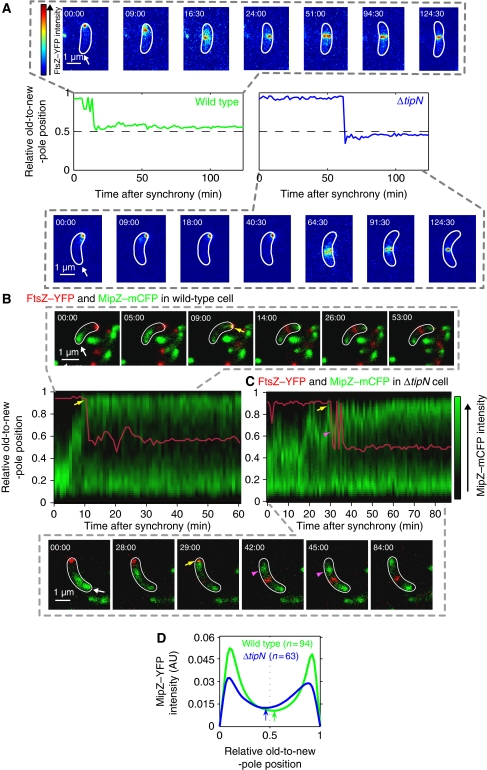
Figure 1.
FtsZ and MipZ dynamics in wild-type and ΔtipN cells. (A) Time-lapse microscopy of FtsZ–YFP in wild-type (MT199) and ΔtipN (CJW2563) cells after synchrony. The expression of ftsZ–yfp was induced with 0.5 mM vanillic acid 2.5 h before synchronization and imaging. Images were acquired every 1.5 min and the cells were identified using MicrobeTracker. The FtsZ–YFP signal in representative wild-type and ΔtipN cells is shown for selected time points as an overlay with the MicrobeTracker cell outline (the old pole is marked by the arrow). The graphs show the trace of the relative FtsZ–YFP position along the cell length over time. (B) Time-lapse microscopy of MipZ–mCFP and FtsZ–YFP in a wild-type background (strain CJW3455). FtsZ–YFP expression was induced with 0.5 mM vanillic acid 1 h before cell synchronization. Time-lapse results from a representative cell are shown as an overlay with MicrobeTracker cell outlines in white (the old pole is marked by the arrow.). The relative position of FtsZ–YFP (red trace) is indicated over a kymograph of the MipZ–mCFP signal profile (green) along the cell length as a function of time after synchrony. Yellow arrows show first instance of MipZ–mCFP and FtsZ–YFP colocalization at the new pole. (C) Same as (B) except in a ΔtipN background (strain CJW3612). Purple arrowheads show backwards motion of MipZ–mCFP. (D) Time-lapse recordings of MipZ–YFP in wild-type (CJW2022) and ΔtipN (CJW3366) cells after synchrony. Images were acquired every 1.5 min and the cells were identified using MicrobeTracker. Shown are profiles of the mean MipZ–YFP signal along the cell long axis of 94 wild-type cells (green) and 63 ΔtipN cells (blue) from the time point when MipZ–YFP becomes bipolar (yellow arrow in (B) and (C) to the onset of cell constriction). The arrows show the minima in MipZ–YFP intensity for each strain.