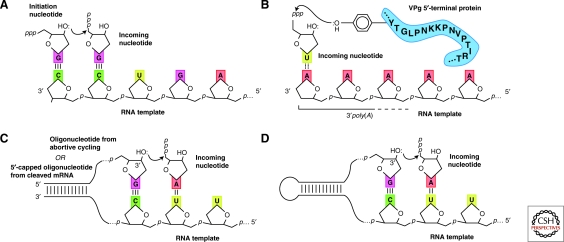
Figure 5.
Comparison of initiation mechanisms. (A) Primer-independent (de novo) initiation B, C, and D—Primer-dependent initiation strategies: (B) “Borrowing” a hydroxyl from a nearby protein residue (C) Use of a short oligonucleotide from abortive cycling in de novo initiation or from a cleaved mRNA; (D) Template folds back to form a stable hairpin that is then extended. Adapted from (Paul et al. 1998; van Dijk et al. 2004 and reprinted with permission from The Journal of General Virology ©2004; Ng et al. 2008 and reprinted with express permission from the authors).