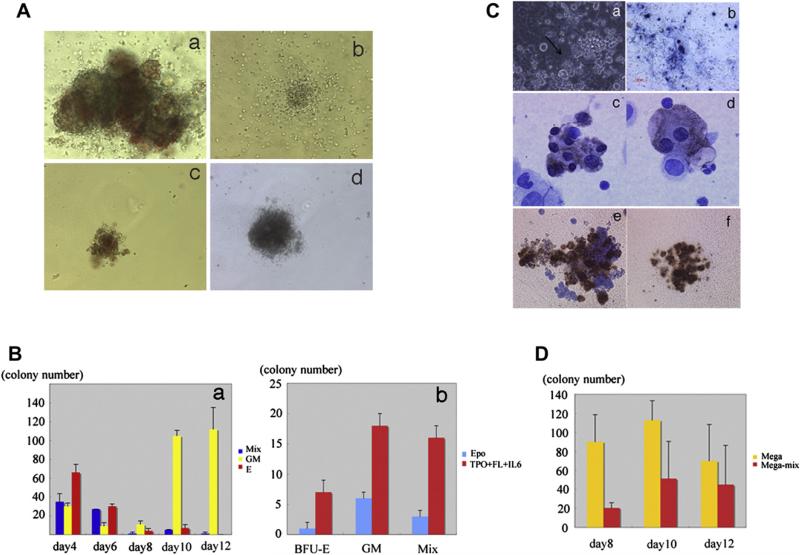
Figure 5.
Colony-forming ability and megakaryocyte potential of mGS Flk1+-derived cells. mGS-derived Flk-1+ cells produce hematopoietic progenitor cells that can form various kinds of colonies [(Aa) mixed colony, (Ab) granulocyte-macrophage (GM) colony, (Ac) burst-forming unit erythroid (BFU-E), (Ad) mast cell colony]. Mixed colonies were predominant when mGS-derived Flk1+ cells were cultured on OP9 cells for 4 to 6 days (Ba). Blue bar: mixed colony, yellow bar: GM colony, red bar: Erythroid colony. The number of all kinds of colonies was increased when mGS Flk1+ cells were cultured on OP9 with thrombopoietin (TPO) and interleukin (IL)-6 (Bb). Blue bar: with erythropoietin (EPO), red bar: with TPO and IL6. Megakaryocyte or proplatelet mGS-derived Flk1+ cells were observed within OP9 culture for 8–12 days. Proplatelet like cells (arrow Ca), Immunostaining of cultured cells with CD41 antibody secondary detected by alkaline phosphatase–conjugated antibody (Cb blue). Immunostaining of a cytospin preparation with CD41 antibody secondary detected by peroxidase conjugated antibody (Cc, Cd brown). After transferring cultured cells into Megacult conditions, megakaryocyte colonies (Cf) include mega-mix colonies (Ce) were found. These cells expressed acethylcholinestrase as evidenced by brown staining. The CFU-Mega was maintained during culturing day 8 to 12 in the presence of TPO and stem cell factor (D). Yellow bar: Megakaryo-colony, red bar: Mega-Mix colony. Magnification: (Ca, Cb) ×100; (Cc, Cd) ×200; (Ce, Cf) ×100.