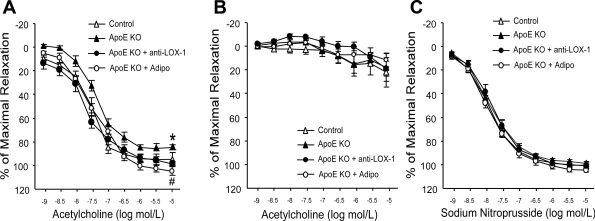
Fig. 1.
Reactivity of the thoracic aorta to ACh in control mice, apolipoprotein E (ApoE) knockout (KO) mice, and ApoE KO mice with anti-lectin-like oxidized LDL (ox-LDL) receptor (LOX)-1 and adiponectin (Adipo) treatment was evaluated. Statistics were conducted on maximal relaxation. A: aortic endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation was impaired in ApoE KO mice versus control mice. Adipo and anti-LOX-1 treatment restored the impaired vasorelaxation in ApoE KO mice. B: vasorelaxation to ACh was abolished in ApoE KO mice treated with either Adipo or anti-LOX-1 after incubation of the aortic rings with the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor NG-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (100 μM for 20 min), which indicated that vasorelaxation to ACh was nitric oxide mediated in aortas. C: endothelium-independent vasorelaxation was comparable among groups. Data are means ± SE; n = 6–7 mice. *P < 0.05 vs. control mice; #P < 0.05 vs. ApoE KO mice.