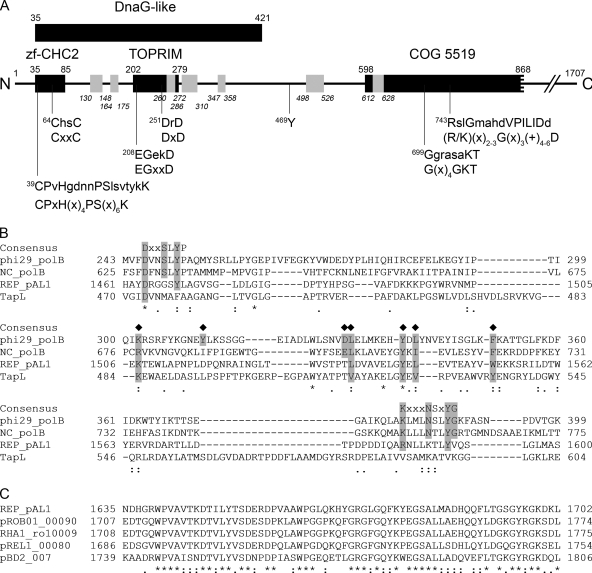
FIG. 1.
Bioinformatic analysis of the REPpAL1 protein. (A) Hypothetical domain architecture and predicted sequence motifs of the N-terminal region of the REPpAL1 protein. The amino acid sequence of REPpAL1 (the gene product of pAL1.101; accession no. CAL09956) is represented by a line. The black bars, with residue numbers above each bar, indicate predicted conserved domains, namely, a DnaG-like domain (COG 0358; E value, 0.005), a CHC2 zinc finger subdomain (smart00400; E value, 0.001), and a Toprim subdomain (cd01029; E value, 3e-06), located within the DnaG region. A central region matched the N-terminal half of COG 5519, representing a superfamily II helicase and derivatives (E value, 3e-05). Searches for conserved domains against the CDD database were performed using the CD Search tool at NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi), with the low-complexity filter inactivated and an E value threshold of 0.01. Putative conserved amino acid motifs are indicated below the bars (x, any amino acid; +, hydrophobic amino acid); the lower lines indicate the consensus sequence of the respective motif (for references, see the text), and the associated upper lines show the amino acid sequence of REPpAL1, with residues matching the consensus in uppercase. Residue Y469, which is conserved in rhodococcal homologs of REPpAL1, is also indicated. The short bars in gray, with residue numbering in italics, correspond to tryptic peptides of REPpAL1 identified in the cross-linked TPpAL1-REPpAL1 complex. For details, see the text. (B) Alignment of segments of phage φ29 DNA polymerase (phi29_polB; GenBank accession no. ACE96023), type B DNA polymerase of Neurospora crassa (NC_polB; CAA39046), REPpAL1 (REP_pAL1; CAL09956), and telomere-associated protein of S. lividans (TapL; AAO73842). The consensus sequence of motifs A and B of φ29 DNA polymerase, which is conserved among different nucleic-acid-synthesizing enzymes (7), is indicated above the sequences. Residues shaded in gray that are marked with a diamond above the sequence may represent conserved residues of the TPR-1 region, which is specific to protein-priming DNA polymerases (14, 15, 27, 37). (C) Alignment of a region rich in acidic residues, which is highly conserved among REPpAL1 (aa 1635 to 1702) and rhodococcal homologs. pROB01_00090 (BAH55508), putative telomere-binding protein of plasmid pROB01 of R. opacus B4; RHA1_ro10009 (ABH00202), possible transcriptional regulator of plasmid pRHL2 of R. jostii RHA1; pREL1_00080 (BAE45951), putative telomere-binding protein of plasmid pREL1 of R. erythropolis PR4; pBD2_007 (AAP73892), putative regulatory protein of plasmid pBD2 of R. erythropolis BD2. In panels B and C, residues conserved throughout are marked with asterisks, while residues marked with colons and dots are conserved and semiconserved substitutions, respectively.