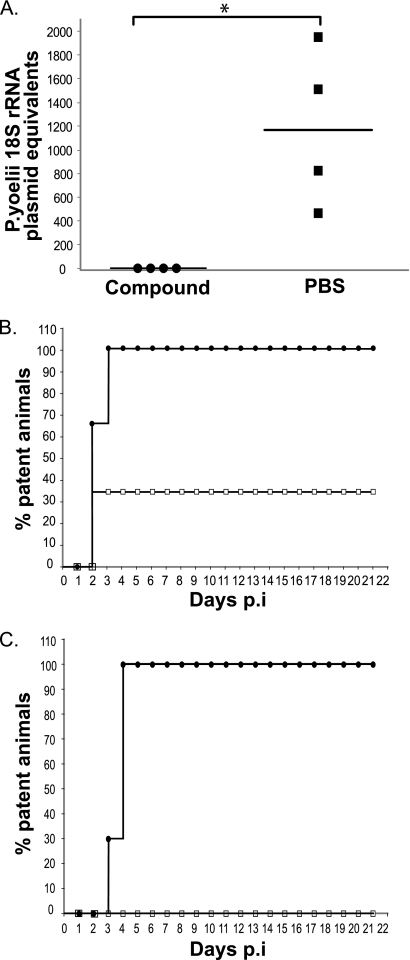
FIG. 3.
A trisubstituted pyrrole inhibits the development of P. yoelii sporozoites into LS in vivo and the appearance of blood-stage parasites. (A) Parasite burden in the livers of mice infected with P. yoelii sporozoites (1 × 104/mouse) and treated with a single dose of either the trisubstituted pyrrole or PBS (n = 4 for each group). Results at 40 h p.i. were determined by parasite-specific quantitative PCR. Infection is expressed as the numbers of copies of P. yoelii 18S rRNA plasmid (*, P = 0.0294 relative to PBS-treated group; Mann-Whitney test). (B) Treatment with a single dose of the trisubstituted pyrrole partially protects from sporozoite infection. Animals were infected with P. yoelii sporozoites (1 × 104/mouse) after receiving a single dose of either the trisubstituted pyrrole (open squares) (n = 3) or PBS (filled circles) (n = 3). (C) Percentages of animals that were positive for blood-stage infection after infection with P. yoelii sporozoites (5 × 103/mouse) and treatment with three doses of either the trisubstituted pyrrole (open squares) (n = 10) or PBS (filled circles) (n = 10).