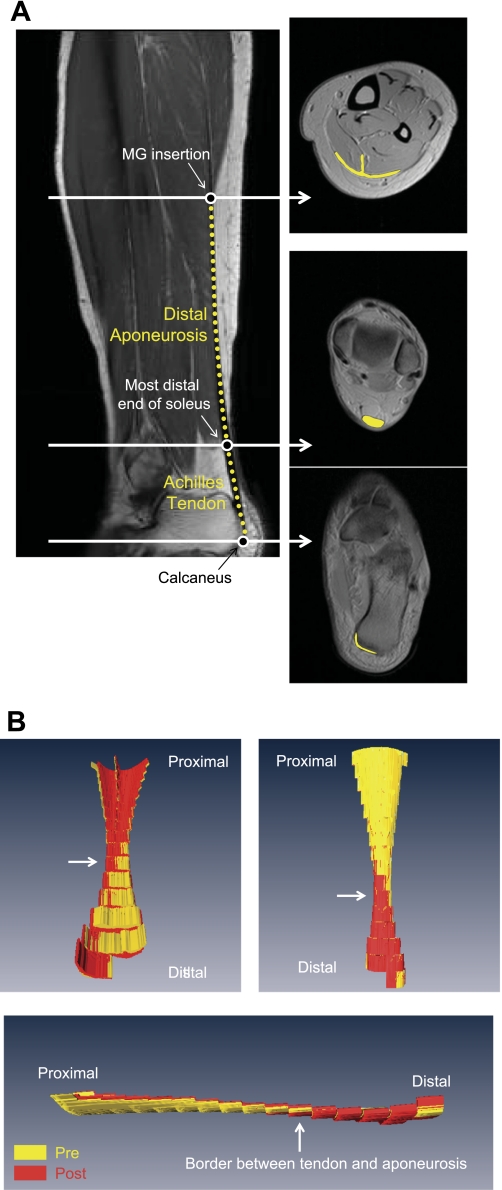
Fig. 1.
Representative oblique sagittal and axial morphological magnetic resonance (MR) images at rest (A) and typical examples of three-dimensional (3D) volume-rendered images of the Achilles tendon and distal aponeurosis in three different views (B). A: white arrows in sagittal image correspond to positions at three different axial images. The Achilles tendon is the segment between the most distal portion of the soleus (middle circle symbol on left) and the calcaneus (bottom circle symbol on left). The distal aponeurosis is the segment between the medial gastrocnemius (MG) insertion region (top circle symbol on left) and most distal portion of the soleus. Achilles tendon and distal aponeurosis are indicated by yellow lines both in the sagittal (dotted) and axial images (solid). There are some inaccuracies in calculating the tendon volume from the acquired MR images since it is difficult to define the most distal edge of the Achilles tendon, particularly as a clearly delineated line, since the Achilles tendon in reality “merges” into the calcaneus progressively. B: typical examples of 3D volume-rendered images of the Achilles tendon and distal aponeurosis in three different views. Achilles tendon and distal aponeurosis were volume rendered from axial morphological MR images. Yellow and red indicate pre- and post-unilateral lower limb suspension (ULLS), respectively.