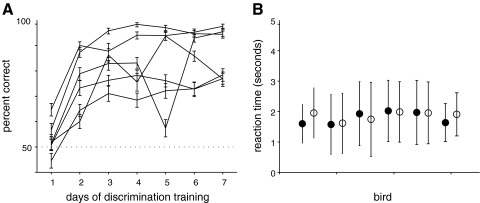
Fig. 5.
Learned discrimination of songs with different durations. A: learning curves for 6 naive birds trained to discriminate songs that differed only in duration. Mean ± SD of percent correct are shown for each day. Birds were trained to discriminate 50 versions of the original B song, compressed to 76% of the original duration, from the 50 versions of the same B songs expanded to 164% of their original duration. These two manipulations were chosen because when birds were asked to categorize songs of two different individuals, the responses to these compressed and expanded songs were not significantly different from responses to the original songs. When explicitly trained to discriminate based on duration, all birds learned to discriminate better than chance by the 2nd day of training. B: mean ± SD of reaction time for compressed (●) and expanded (○) songs for all birds. There was no significant difference in reaction time for the two different song types.