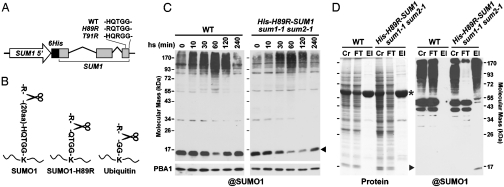
Fig. 1.
Use of the His-H89R-SUMO1 variant to enrich for SUMO1 conjugates in Arabidopsis. (A) A schematic of the His-H89R-SUM1 transgene. Lines indicate introns. Black and gray boxes represent 6His and SUMO1 coding regions, respectively. The C-terminal sequences of the T91R and H89R variants are shown. (B) Diagrams of the trypsin footprints generated from proteins modified with SUMO1, H89R-SUMO1, and Ub. (C) Accumulation of SUMO conjugates during and after a 30 min heat stress (37 °C) of wild-type (WT) and His-H89R-SUM1 sum1-1 sum2-1 seedlings. Crude extracts were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-SUMO1 or anti-PBA1 antibodies (loading control). (D) Enrichment of SUMO1 conjugates from His-H89R-SUM1 sum1-1 sum2-1 plants by Ni-NTA affinity chromatography. The crude extracts (Cr), column flow through (FT), and eluates (El) from WT and rescued lines were separated by SDS/PAGE and stained for total protein (Left) or subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-SUMO1 antibodies (Right). ▸, free His-H89R-SUMO1. *, large subunit of RUBISCO.