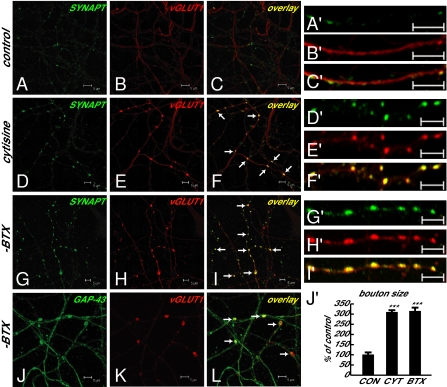
Fig. 4.
Glutamatergic presynaptic boutons containing α-synaptophysin are significantly enlarged and are largely en passant boutons. (A–C and A′–C′) α-Synaptophysin and vGLUT1 immunoreactivities in control cultures. (D–I and D′–I′) Colocalization of α-synaptophysin in increased and enlarged vGLUT1-positive glutamatergic presynaptic boutons in cytisine- or α-BTX–treated cultures. (J–L) Glutamatergic presynaptic boutons (vGLUT1 as glutamatergic presynaptic terminal marker) along axons (GAP-43 as axonal marker) in α-BTX–treated cultures. (Scale bars as indicated.) (J′) Quantitative measurement of bouton size, showing significant enlargement of glutamatergic boutons containing both α-synaptophysin and vGLUT1 in cytisine-treated (1.21 ± 0.05 μm2, n = 61, P < 0.001 vs. control) or α-BTX–treated (1.23 ± 0.06 μm2, n = 60, P < 0.001 vs. control) cultures compared with those in control cultures (0.39 ± 0.04 μm2, n = 31). n, Number of boutons in three to four fields from different cultures in each group. (Scale bars, 5 μm.)