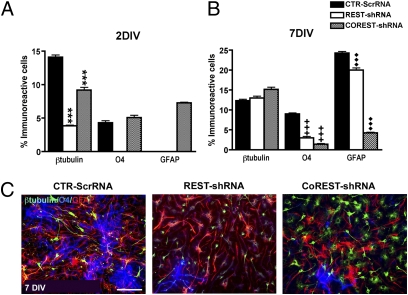
Fig. 3.
Effects of selective REST and CoREST depletion on NSC-mediated neurogenesis and gliogenesis. (A) The percentage of β-tubulin+ clones at 2 and 7 d in vitro (DIV) reveals that REST and CoREST are differentially required for neurogenesis. Analysis of O4+ clones reveals that REST and CoREST differentially regulate OL lineage elaboration and maintenance. Analysis of GFAP-immunoreactive clones reveals that REST and CoREST also have selective effects on the generation and maintenance of ASs. Bars in A and B represent the mean ± SEM of three independent biological replicates. ***, +++, and ♦♦♦P < 0.0001. (C) Immunofluorescence microscopic analysis demonstrates the lineage composition of secondary clones derived from NSCs following selective ablation of REST or CoREST compared with the control condition. Neural lineage markers were used to identify neurons (β-tubulin, FITC), oligodendrocytes (O4, DAPI), and astrocytes (GFAP, TRITC). (Scale bar, 200 μm).