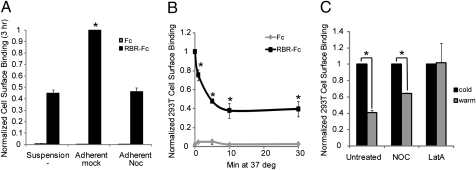
Fig. 3.
The cell adhesion-dependent differential of RBR binding to the cell surface depends on microtubules and actin filaments. (A) Suspension 293F cells were mock treated or treated with nocodazole (Noc; 10 μM) for 1 h and then examined under three conditions: continued growth in suspension or plated for 3 h on fibronectin-coated dishes in the presence or absence of 10 μM nocodazole. Cells were then chilled, lifted by pipetting with cold PBS++, and assessed for RBR binding as described previously (assay done at 4 °C) (6, 8). Data bars represent the average of triplicate samples from one experiment. Statistical significance compared with the suspension mock-treated sample was determined by Student t test (*P < 0.004). (B) Adherent 293T cells were lifted as in A at 4 °C and then incubated at 37 °C (to allow membrane trafficking). At the indicated times, cells were chilled and then examined for RBR binding as described in A. (C) Adherent 293T cells were left untreated or treated with 10 μM Noc or 1 μM latrunculin A (LatA) for 1 h. All samples were then lifted at 4 °C and either kept at 4 °C (cold) or incubated at 37 °C for 30 min (warm) in the presence or absence of inhibitor. Cells were then examined for RBR binding as above. In B and C, data points represent the averages of at least three experiments (performed in duplicate) normalized to the level of RBR binding to the surface of cells kept on ice for the duration of the experiment (labeled 0 min in B and cold in C). Error bars represent SD of the normalized data. Statistical significance compared with the 0 min/cold sample was determined by Student t test (*P < 0.05).