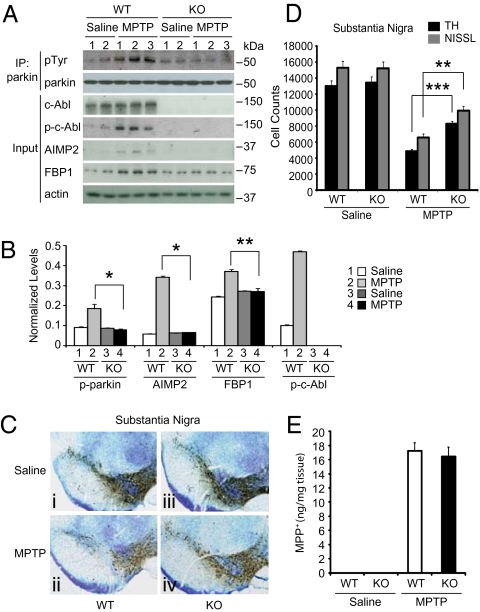
Fig. 5.
c-Abl knockout (KO) protects against MPTP-induced loss of DA neurons. (A) c-Abl KO prevents parkin tyrosine phosphorylation and the accumulation of AIMP2 and FBP1 in the striatum of MPTP-treated mice. Immunoblots of Parkin immunoprecipitation samples from WT and c-Abl KO littermates treated with saline or MPTP (four i.p. injections. 20 mg/kg, at 2-h intervals). Immunoblotting with an anti-phosphotyrosine antibody shows tyrosine-phosphorylated parkin and an anti-parkin antibody shows immunoprecipitated parkin. Brain lysates were immunoblotted with anti-phospho-c-Abl to show tyrosine-phosphorylated c-Abl, an anti-actin antibody was used as a loading control, and AIMP2 and FBP1 antibodies were used to monitor their levels. (B) Normalized levels of tyrosine-phosphorylated parkin (p-parkin), AIMP2, FBP1, and phospho-c-Abl (p-c-Abl). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM and were evaluated for statistical significance by one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (C) Photomicrographs of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-immunostained sections in the substantia nigra of WT (a and b) and c-Abl KO (c and d) littermate mice treated with vehicle (a and c) and MPTP (b and d). (D) Number of TH- and Nissl-positive neurons in the substantia nigra of WT and c-Abl KO littermate mice treated with PBS vehicle and MPTP, determined by stereological counting. The data are the mean ± SEM (n = 6). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc test. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (E) Levels of MPP+ in the striatum of WT and c-Abl KO mice treated with PBS vehicle and MPTP (four i.p. injections. 20 mg/kg, at 2-h intervals) 90 min after final injection. All experiments were repeated three times and representative images of the immunoblots are shown.