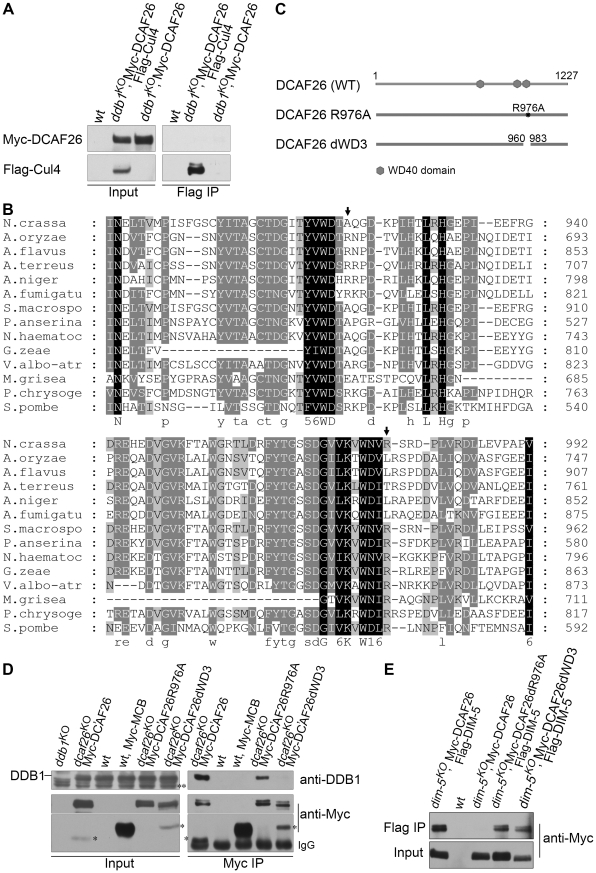
Figure 5. WD3 region of DCAF26 is necessary for binding between DCAF26 and DDB1.
(A) Immunoprecipitation assay with Flag antibody showing that Flag-Cul4 failed to form a complex with Myc-DCAF26 in the ddb1KO strain. (B) Amino acid alignment of the conserved WD40 regions and WDXR motifs of different fungi DCAF26 homologs. The identical residues among different homologs are shaded. Arrows point out the arginine in the WDXR motif. (C) Graphic diagrams showing the domain structure of DCAF26 and different DCAF26 internal point mutations or deletion mutants. (D) Immunoprecipitation assay with c-Myc antibody showing that Myc-DCAF26 failed to interact with DDB1 in the DCAF26dWD3 mutant, but not in the DCAF26R976A mutant, compared to the strong interaction between DDB1 and wild-type DCAF26. Double asterisks indicate nonspecific bands detected by anti-DDB1 serum. Asterisks indicate degraded species of Myc-DCAF26. (E) Immunoprecipitation assay with Flag antibody showing that the mutant Myc-DCAF26 in the DCAF26R976A and DCAF26dWD3 strains still interacted with Flag-DIM-5.