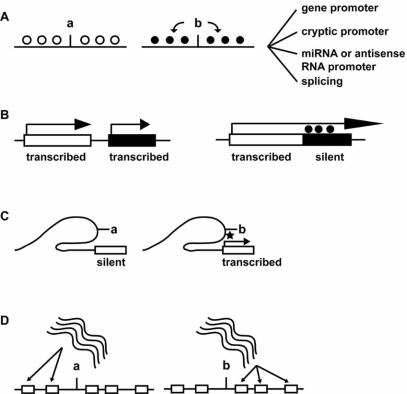
Fig. (1).
Schematic effects of GV on epigenetic marks. A, allele (a and b, respectively)-specific regulation of local DNA methylation states and examples of possible biological effects. Vertical lines mark GV position. Open and closed circles represent unmethylated and methylated residues, respectively. The b allele is hypothetically represented as the one associated with DNA hypermethylation spreading to adjacent sequences (arrows). B, normal expression patterns of two adjacent genes (left) are altered if a deletion in polyadenylation signal sequence of the upstream gene causes transcript extension to and silencing of a downstream gene (right). Closed circles on the right indicate hypermethylation of the overrun promoter of the downstream gene. C, long-range transcriptional impact of GV-associated epigenetic marks. The b allele is associated with enhancer-like histone marks (star) positioned in a chromatin loop extending to a gene promoter (white rectangle). D, noncoding SNP-containing transcripts (curved lines) regulate expression and epigenetic marks of different target genes (white boxes) depending on genotype. See [2,58,59,63,64,72] and text for details.