Figure 2.
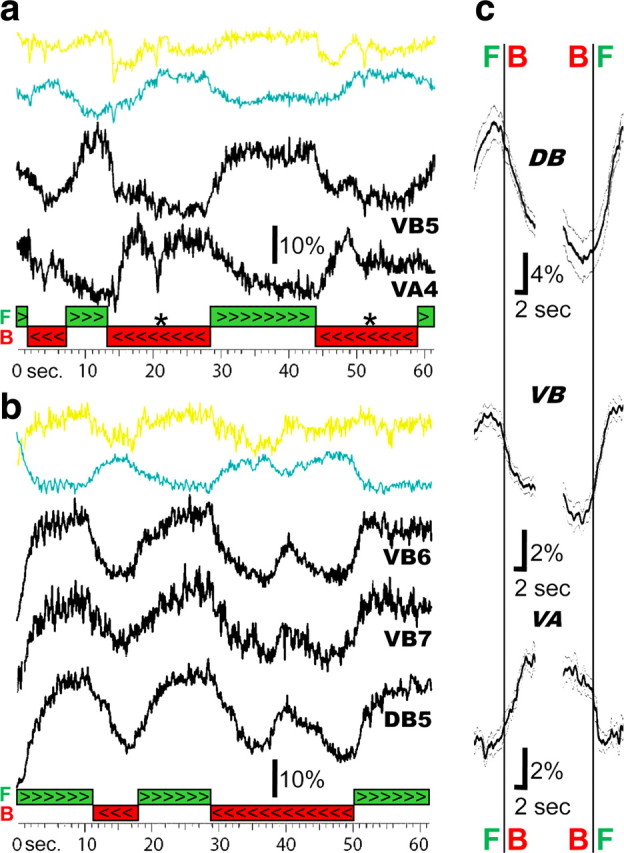
B-motoneurons are active during forward semirestrained locomotion while A-motoneurons are active during backward. a, The top two colored traces are the signals from the yellow and cyan channels recorded from a VB5 motoneuron. The ratio of the yellow/cyan signal is shown underneath these traces together with the ratio signal from a VA4 motoneuron during forward (green bar ⋙) and backward (red bar ⋘) locomotion. The asterisk (*) marks a period when locomotion stopped. b, Dorsal and ventral B-motoneurons, The raw yellow and cyan traces and their ratio recorded from a VB6 motoneuron (yellow and cyan and uppermost black traces) together with the activity of a VB7 motoneuron (middle black trace) and a DB5 motoneuron (bottom black trace) during forward (green bar >>>) and backward (red bar <<<) locomotion. c, Mean ratio change during the switch from forward to backward (left traces) and backward to forward (right traces) locomotion. All ratiometric recordings were aligned by the time of the independently scored changes in direction determined from the behavior video. The number of transitions used to compute the averages were as follows: forward to backward, 12 (DB), 60 (VB), 23 (VA); backward to forward, 13 (DB), 55 (VB), 18 (VA). Gray traces are one SEM.
