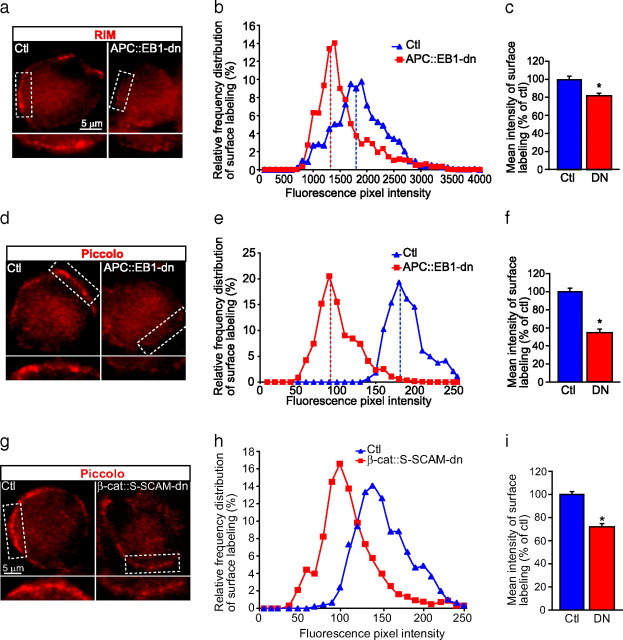
Figure 9.
a–i, Presynaptic active zone protein clusters are decreased in terminals that contact postsynaptic neurons expressing APC::EB1-dn or β-cat::S-SCAM-dn. a, d, g, Micrographs of immunofluorescence double-labeled E11–E13 CG frozen sections showing that RIM (red; a) and piccolo (red; d, g) clusters are decreased in presynaptic terminals that contact postsynaptic neurons expressing APC::EB1-dn (a, d) or β-cat::S-SCAM-dn (g) compared with terminals on Ctl neurons. Insets, Twofold magnification views of boxed regions. b, c, e, f, RIM (b, c) and piccolo (e, f,) clusters show shifts to lower pixel intensity levels (b, e) and reductions in mean intensity levels of 18.8% for RIM (c) and 48.2% for piccolo (f) in presynaptic terminals on APC::EB1-dn neurons relative to terminals on Ctl neurons. (RIM, c; *p < 7.6 × 10−4, Student's t test; n = 28 DN and 49 Ctl neurons; piccolo, d; *p < 8.9 × 10−24, Student's t test; n = 27 DN and 10 Ctl neurons). Similarly, piccolo staining shows 28% reductions in mean intensity levels (h, i) in presynaptic terminals on β-cat::S-SCAM-dn-expressing neurons (i, *p < 6.5 × 10−13, Student's t test; n = 24 DN and 24 Ctl neurons). Dashed vertical lines indicate the median intensity values (b, e, h). Bars represent the mean ± SEM (c, f, i).