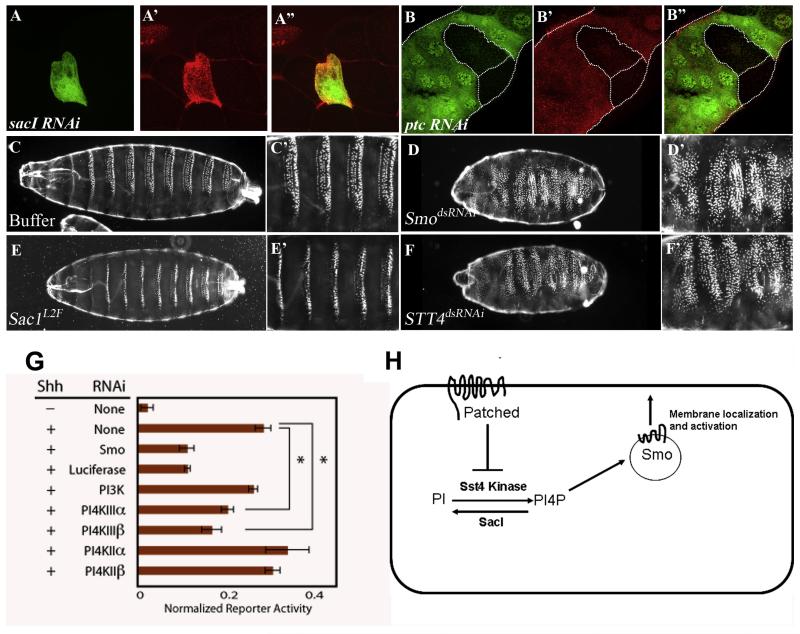
Figure 6. STT4 kinase and SacI phosphatase function in Hh signaling.
(A-A”) Loss of sacI function in positively marked flip-out clones (A, green) generated using the Ay-Gal4 UAS-sacI RNAi combination in salivary gland shows elevated levels of PI4P (A’, red). The merged panel is shown in (A”).
(B-B”) Loss of ptc function in positively marked flip-out clones (B, green) generated using the Ay-Gal4, UAS-ptcRNAi combination in salivary gland shows elevated levels of PI4P (B’, red). The merged panel is shown in (B”). The outline of the salivary gland and wild-type cells are marked with white dotted line.
(C-C’) Organization of denticle belts in wild-type Drosophila embryo microinjected with buffer. A higher magnification of panel (C’) emphasizes normal polarity of denticle belts.
(D-D’) Denticle belt preparation from embryo microinjected with smodsRNAi. The denticle belt pattern is disrupted with the broadening of each belt and a loss in its polarity (magnified image in D’).
(E-E’) sac1L2F /sac1L2F homozygous embryo showing reduction in denticle belt specification, a phenotype similar to that seen in weak ptc mutant embryos.
(F-F’) Denticle preparation of microinjected embryo with STT4dsRNAi showing expansion of denticle belt specification similar to that seen in smodsRNAi (compare with D-D’)
(G) PI4III kinase RNAi inhibits Hh pathway activation in mammalian cells.
Diced siRNA pools were made against PI4III kinase α and PI4III kinase β, the mammalian STT4 and PIK1 homologs, respectively.4 RNAi against other PI4 kinases and PI3 kinase were also tested, along with RNAi against Smo. Hh reporter cells were treated with the indicated RNAi, then grown to confluency and switched into low serum growth medium containing Shh. Following 24 h Shh treatment, cells were lysed and assayed for firefly luciferase-based reporter induction relative to a constitutive Renilla luciferase. Data is reported as the mean of three replicates +/− one standard deviation. *p<0.01, Student’s t-test (two-tailed).
(H) A model. The genetic results presented here are consistent with a model in which Ptc inhibits PI4P formation and this causes retention of Smo away from the plasma membrane. Hh binding to Ptc would activate STT4 kinase and the increase of PI4P will cause a non-stoichiometric amount of Smo to be transported to the cell membrane.