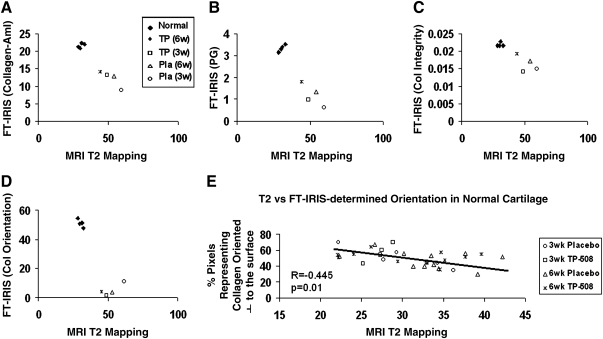
FIG. 6.
Correlation between FT-IRIS–derived parameters and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T2 values. (A) T2 relaxation (ms) versus collagen–amide (Am) I content, (B) T2 relaxation (ms) versus PG content, (C) T2 relaxation (ms) versus collagen integrity (new tissue formation), and (D) T2 relaxation (ms) versus % pixels representing collagen fibers oriented perpendicular to the articular surface. This percentage was calculated from the polarized FT-IRIS image by dividing the pixels into three orientation categories (parallel to surface, random, and perpendicular to surface) according to Am I/Am II ratio values. The percentage of pixels falling into each category was then calculated. All normal native hyaline articular cartilage demonstrated greater FT-IRIS–determined values for Am I, PG, and collagen integrity parameters, and perpendicularly oriented collagen fibrils, and shorter T2 relaxation times compared to repair tissue, regardless of treatment. (E) There was a significant inverse correlation in normal cartilage between the % of pixels representing collagen oriented perpendicular to the articular surface and T2 relaxation. ♦, normal cartilage; ×, TP-508 (6-week repair); □, TP-508 (3-week repair); ▵, placebo (6 week repair); ◊, placebo (3 week repair).