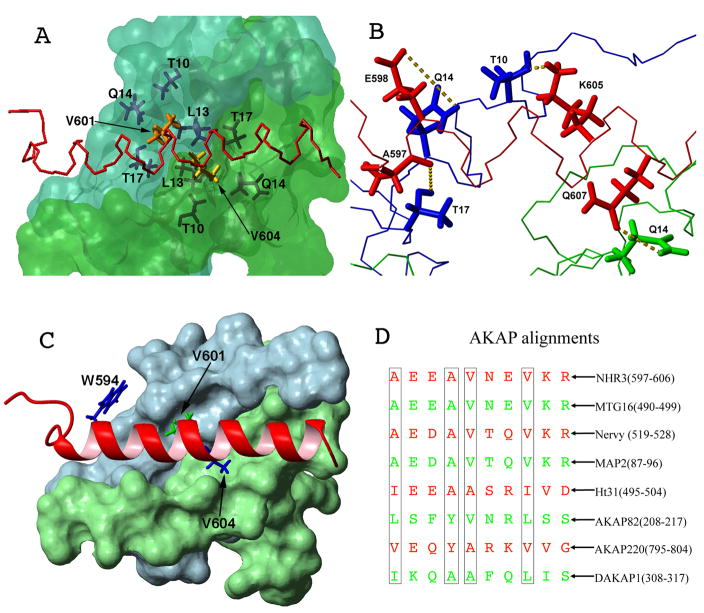
Figure 3. Residues important for NHR3/PKA (RIIα) binding.
(A) Surface representation of the PKA (RIIα) dimer (blue: protomer one, green: protomer two) with a line representation of NHR3 (red). Residues that form hydrophobic pockets in PKA (RIIα) are shown in dark blue and dark green line representations. Residues V601 and V604 of NHR3 are shown in orange and yellow, respectively.
(B) Line representation of PKA (RIIα) dimer (blue: protomer one, green: protomer two) with a line representation of NHR3 (red). Hydrogen bonds formed between residues of PKA (RIIα) and NHR3 are shown as yellow dotted lines.
(C) Surface representation of the PKA (RIIα) dimer (blue: protomer one, green: protomer two) with a ribbon representation of NHR3 (red). Residues in NHR3 selected for alanine mutations are highlighted.
(D) Alignment of AKAP homologues including the NHR3 domain of ETO and other ETO homologs. Residues important to the PKA (RIIα) interaction shown in boxes.