FIGURE 3.
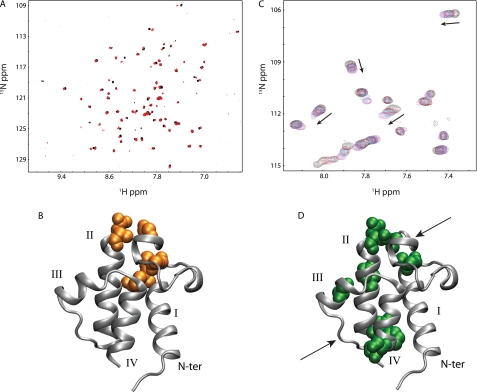
Divalent cation binding to wild-type and A75H V. harveyi ACP. A, natural abundance HSQC spectra of wild-type V. harveyi ACP in the presence of calcium (red) and magnesium (black) ions suggest ACP adopts similar conformations in the presence of either divalent cation. B, VhACP A75H structure showing in orange where the residues display the largest chemical shift differences in the presence of the two cations. C, HSQC spectra of VhACP A75H collected at 0, 0.3, 0.5, 0.9, and 4.0 mm CaCl2 (black, red, blue, cyan, magenta, respectively) indicate that calcium binding occurs on the fast NMR timescale for both sites (see arrows). Only a portion of the HSQCs are shown for clarity. D, residues affected the most upon addition of calcium are highlighted in green, spatially matching the E. coli ACP divalent cation-binding sites (arrows).