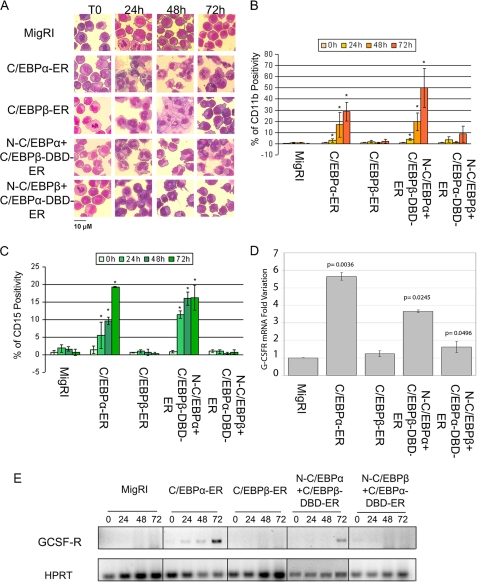
FIGURE 2.
Effects of wild-type and chimeric C/EBP proteins on differentiation of K562 cells. A, morphology is shown. Light microscopy images of May-Grünwald-stained, untreated or 4-HT-treated K562 cells are shown; original magnification ×40. Counts of differentiated cells, summarized in Table 1, were performed in at least 10 fields. B, CD11b positivity is shown. C, CD15 positivity is shown. Values represent the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. * p < 0.05 relative to MigRI transduced K562 cells. GCSF-R mRNA expression was assessed by real time-Q-PCR (D) or semiquantitative RT-PCR (E) in 4-HT-treated (24 h in panel D; 24, 48, and 72 h in panel E) K562 cells retrovirally transduced with MigRI or cDNAs encoding wild-type or chimeric C/EBP proteins. HPRT expression was used as internal control in both PCR. In panel D results are reported as normalized -fold variation of the expression of G-CSFR mRNA; values are expressed as -fold variation relative to expression in the 4-HT-treated empty vector-transduced sample taken as 1. HPRT expression was used as the internal loading control. Error bars denote S.D. of normalized means of two independent experiments performed in triplicate.