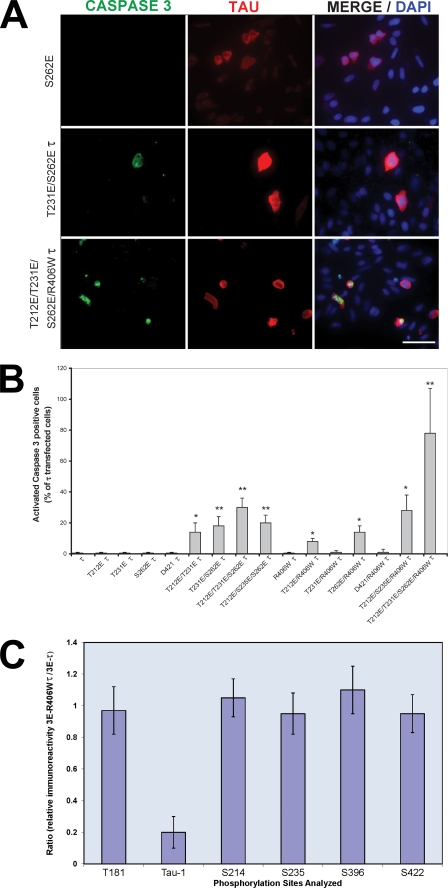
FIGURE 5.
Caspase activation in Tau-transfected CHO cells. A, cells were transfected with pseudophosphorylated wild type and R406W-mutated Tau proteins. After 48 h, the cells were double labeled with 134d (Tau) and activated caspase-3. Cells were counterstained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei. Bar, 50 μm. B, quantification of cells double stained for Tau and activated caspase-3. Approximately 300 cells were counted in each transfection. T212E/T231E/S262E/R406W Tau induced the highest caspase activation in the transfected cells. Error bars, SD. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; Error bars, SD. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. C, cells were transfected with T212E/T231E/S262E Tau or T212E/T231E/S262E/R406W Tau. (After 48 h, the cells were harvested, and phosphorylation of Tau at different sites (Thr181, Ser199/202 (Tau-1), Ser214, Ser235, Ser396, and Ser422) was determined by quantitative immuno-dot blots using antibodies specific to total and different phospho-Tau proteins.) The results are shown as the ratio of the immunoreactivity for T212E/T231E/S262E/R406W Tau (3E R406W Tau) to T212E/T231E/S262E Tau (3E Tau). No significant differences (p < 0.5) were found in the sites investigated between 3E Tau and 3E R406W Tau, with the exception of the Tau-1 site (reactive when Ser198/199–202 are not phosphorylated); Error bars, SD.