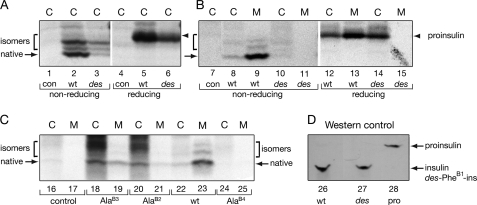
FIGURE 9.
Pulse-chase studies of proinsulin analogs in HEK293T cells. A, the newly synthesized wild-type or des-PheB1-human proinsulin from transfected HEK293T cells (C) were immunoprecipitated as described in the legend to Fig. 8 and analyzed by Tris-Tricine-urea-SDS-PAGE under non-reducing (lanes 1–3) and reducing (lanes 4–6) conditions. con (lanes 1 and 4) denotes empty vector control. des-PheB1-Human proinsulin presented mostly as misfolded disulfide isomers. Reduction leads to coalescence of native and non-native disulfide isomers as a single band (arrowhead). On reduction, wild-type and variant proinsulin exhibit similar electrophoretic mobilities; extent of expression of variant (lane 6) is reduced relative to wild-type (lane 5). B, aliquots of cells from panel A were chased for 2 h and analyzed under non-reducing and reducing conditions. Whereas the majority of wild-type proinsulin was secreted from cells (C) to medium (M) after a 2-h chase, the des-PheB1-human proinsulin was barely detectable in the cells (lane 10) under non-reducing conditions and was not secreted. Under reducing conditions, however, the variant protein was recoverable (lane 14), suggesting that it formed aberrant disulfide-linked complexes and was retained in the ER. C, corresponding studies of AlaB2, AlaB3, and AlaB4 variant proinsulins analyzed under non-reducing conditions demonstrate a range of perturbations: AlaB4, severe; AlaB2, moderate, and AlaB3, partial impairment of biosynthesis and secretion. D, control Western blot for specificity of antiserum. Aliquots (100 ng) of human insulin (lane 26), des-PheB1-insulin (lane 27), and human proinsulin (lane 28) were resolved under non-reducing conditions, transferred onto a nitrocellular membrane, and blotted with guinea pig anti-porcine insulin antibody. This Western blot indicated that the antibody recognized the three proteins with similar efficiencies.