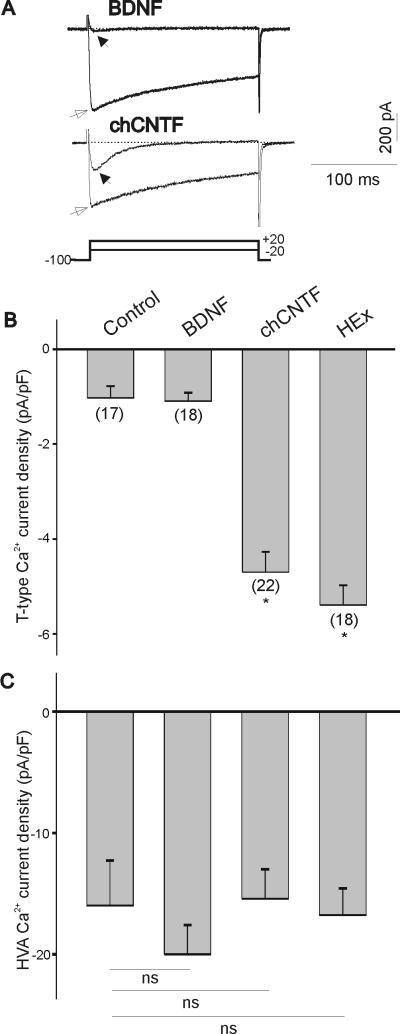
Figure 1.
Effect of BDNF, chick CNTF and heart extract on T-type Ca2+ channel expression in vitro. A) Representative traces of inward Ca2+ currents of E7 nodose neurons cultured for 24 hr with BDNF (50 ng/mL) or chCNTF (50 ng/mL). T-type Ca2+ currents were generated by a 200 ms depolarizing pulses to −20 mV from a holding potential of −100 mV (filled arrows). HVA Ca2+ currents were generated by a 200 ms depolarizing pulse to +20 mV from a holding potential of −100 mV (empty arrows). Stimulation protocol for both T-type and HVA Ca2+ currents is shown in bottom trace. B) Mean T-type Ca2+ current densities after 24 hr treatment with BDNF, chCNTF and heart extract as compared with acutely isolated E7 nodose neurons (control). Current densities were obtained by dividing current amplitude by cell capacitance. Note little differences in T-type Ca2+ current densities between acutely isolated and BDNF-treated neurons. Culture of nodose neurons with chCNTF or heart extract evokes a significant increase in T-type Ca2+ current densities (* denotes p ≤ 0.05 vs. BDNF). C) Culture of E7 nodose neurons with BDNF, chick CNTF or heart extract does not alter mean HVA Ca2+ current densities (ns=not significant).