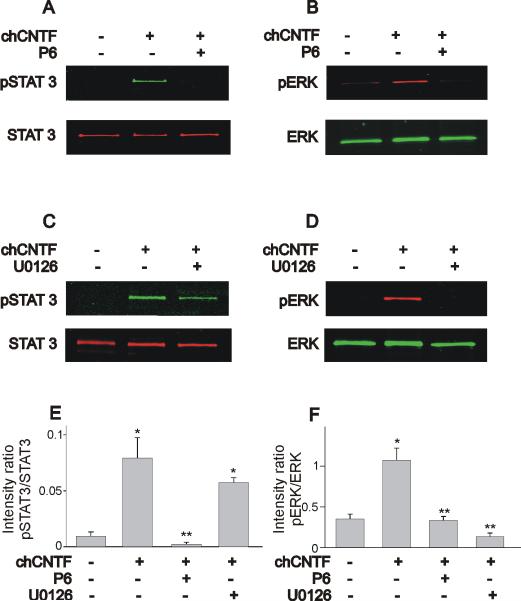
Figure 4.
Effect of the JAK inhibitor P6 and the ERK inhibitor U0126 on STAT3 and ERK phosphorylation in nodose neurons. A, B) Chick CNTF evoked activation of STAT3 and ERK is blocked by the inhibitor of JAK kinases P6 (10 μM). C, D) The ERK inhibitor U0126 (50 μM) only blocks ERK phosphorylation but does not affect STAT3 activation. E, F) Effect of P6 and U0126 on the pSTAT3/STAT3 and pERK/total ERK intensity ratio. Stimulation of nodose neurons with chCNTF caused a significant increase in the pSTAT3/total STAT3 ratio. Notice that only P6 but not U0126 caused a significant reduction in the pSTAT3/STAT3 intensity ratio. Stimulation of nodose neurons with chCNTF also caused a 3-fold increase in the pERK/total ERK ratio. Treatment with either P6 or U0126 inhibits the stimulatory effect of chCNTF on ERK phosphorylation (n= 3–5). In these experiments, nodose neurons were isolated at E7 and pre-treated with P6 (or U0126) for 1 hr prior exposure to chCNTF for 30 min. * denotes p ≤ 0.05 vs. control (no treatment), ** denotes p ≤ 0.05 vs. CNTF treatment for 30 min.