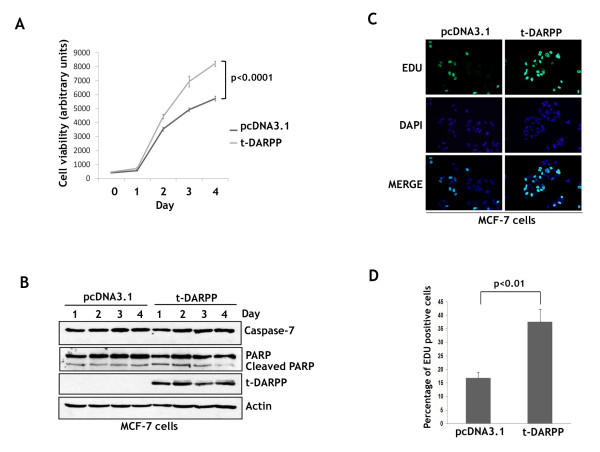
Figure 2.
t-DARPP ectopic overexpression promotes breast cancer cell growth and proliferation. A, MCF-7 cells were stably transfected with t-DARPP or pcDNA3.1 empty vector control plasmids. The cells (2 × 103 cells per well) were seeded onto 96-well culture plates and grown for 1, 2, 3, and 4 days and then subjected to Cell Titer-Glo Luminiscent Cell Viability Assay. Growth rate of MCF-7 cells stably expressing t-DARPP (grey color) was significantly higher (p < 0.0001) than empty vector control cells (black color). B, the cells (2 × 105 cells per well) were seeded onto 6-well culture plates and grown for 1, 2, 3, and 4 days. Protein extracts from these cell cultures were subjected to western blot analysis of t-DARPP, Caspase-7, PARP, and β-actin. The results indicated that t-DARPP-induced cell growth over 4 days was not affected by apoptosis as shown by Caspase-7 and PARP. C, MCF-7/pcDNA3.1 and MCF-7/t-DARPP cells were grown for 48 h then subjected to the Click-iT EdU proliferation Assay. Proliferating cells were depicted by EdU positive staining (green fluorescence) and all the cells were stained with DAPI (nuclear blue fluorescence). D, a summary of the results showing the percent of proliferating cells. Cell proliferation of t-DARPP-expressing cells (37%) was significantly higher than control cells (16%, p < 0.01). Results are representative of at least three experiments and shown as the mean ± SD. Significance of difference was calculated using Student's t test.