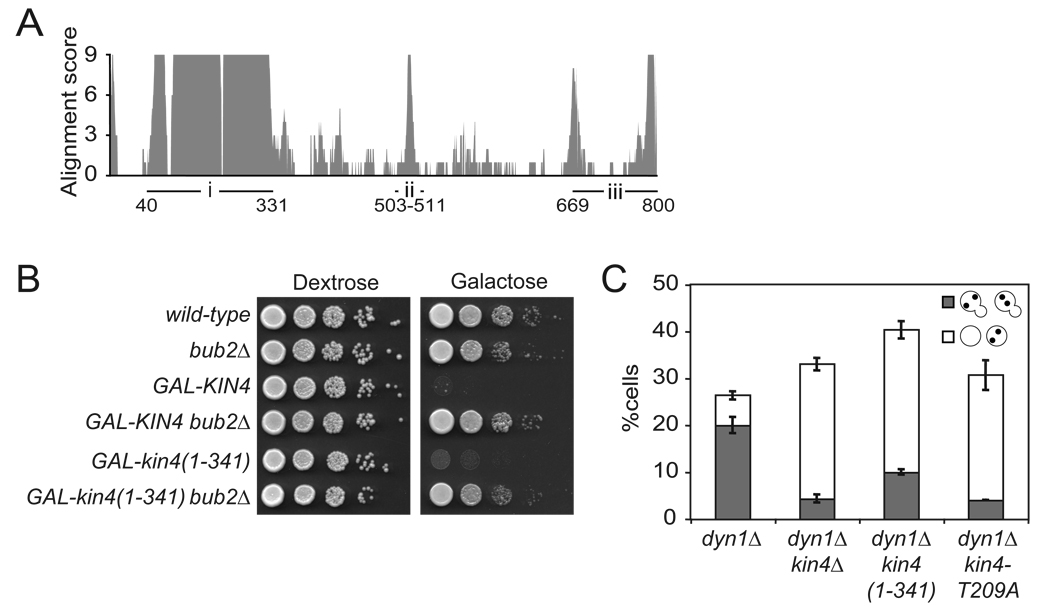
Figure 2. The N-terminal kinase domain of Kin4 mediates MEN inhibition.
(A) The amino acid sequence of Kin4 and its orthologs were aligned using T-Coffee and the alignment score was plotted against the amino acid position. The three major regions of conservation are labeled i, ii and iii with the amino acid positions marked.
(B) Wild-type (A2587), bub2Δ (A1863), pGAL1-10-GFP-KIN4 (A11997), pGAL1-10-GFP-KIN4 bub2Δ (A18792), pGAL1-10-GFP-kin4(1–341) (A23250) and pGAL1-10-GFP- kin4(1–341) bub2Δ (A24113) cells were spotted on plates containing either glucose or galactose and raffinose as in Figure 1A.
(C) dyn1Δ (A17349), dyn1Δ kin4Δ (A17351), dyn1Δ kin4(1–341) (A22262) and dyn1Δ kin4-T209A (A22736) were grown at 14°C for 24 hours. Cells were stained as in Figure 1B. n ≥ 100 cells per sample. Error bars represent SEM.