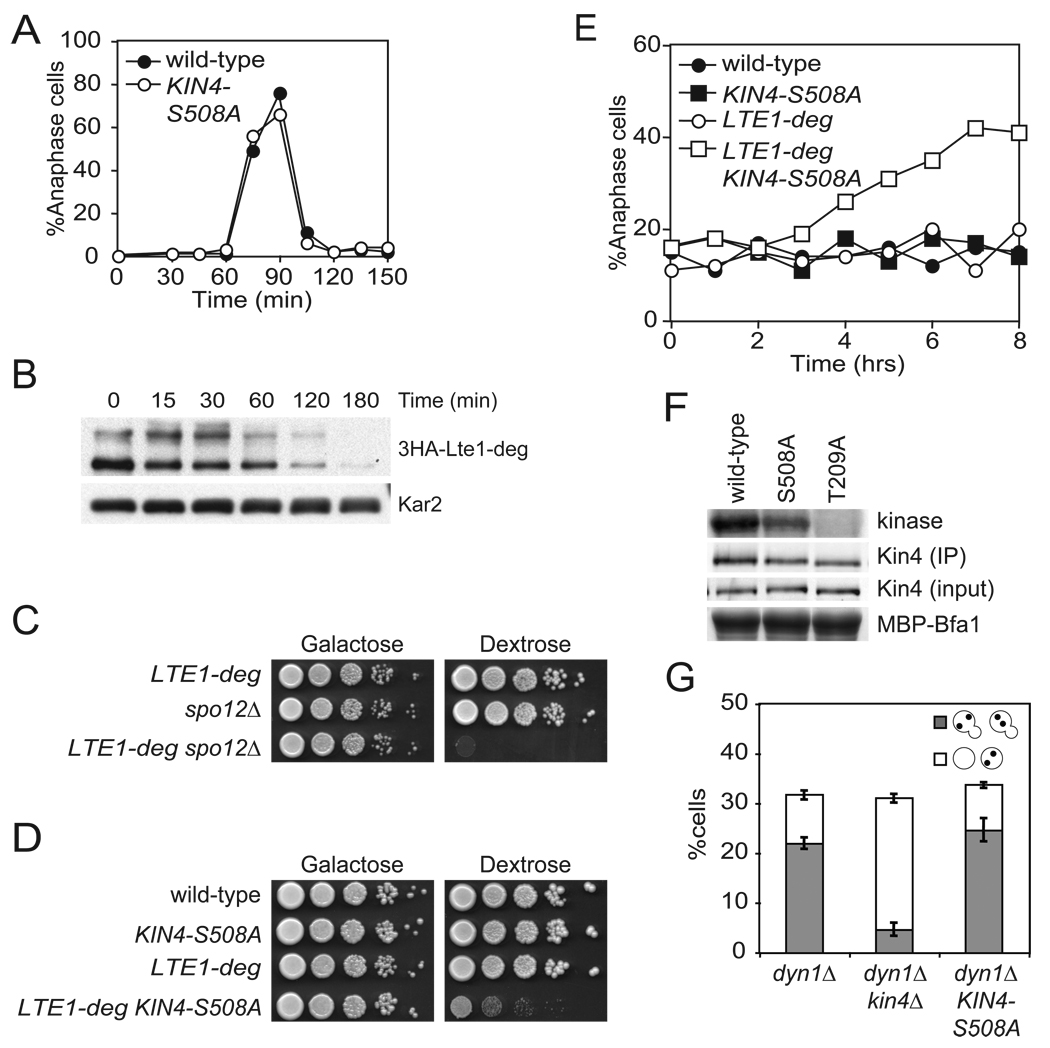
Figure 4. Kin4 localization in the bud delays mitotic exit cells lacking Lte1.
(A) Wild-type (A2587) and KIN4-S508A (A21299) cells were analyzed as in Figure 1B.
(B) Cells expressing a URL-3HA-Lte1 fusion protein (A23686) from the galactose inducible promoter were grown in YePA + 2% raffinose + 2% galactose (YePA+RG) to exponential phase. 2% glucose was added to the media at time = 0 to repress the GAL promoter and samples were collected for western blot analysis. Kar2 was used as a loading control.
(C) pGAL1-10-URL-3HA-LTE1 (LTE1-deg) (A23686), spo12Δ (A4874) and LTE1-deg spo12Δ (A24543) cells were spotted on plates containing either glucose or galactose and raffinose as in Figure 1A.
(D) Wild-type (A2587), KIN4-S508A (A21299), LTE1-deg (A23686) and KIN4-S508A LTE1-deg (A24084) cells were analyzed as in (C).
(E) Cells in (D) were grown as in (B) and samples were collected and analyzed for spindle and nuclear morphology as in Figure 1B.
(F) Cells expressing either Kin4-3HA (A11779), Kin4-S508A-3HA (A20608) or kin4-T209A-3HA (A22119) were grown to exponential phase and arrested with 15 µg/mL nocodazole for 2 hours. Kin4 associated kinase activity (top, Kin4 kinase), immunoprecipitated Kin4-3HA (second row, Kin4 (IP)), total amount of Kin4-3HA in extracts (third row, Kin4 (input)) and the amount of Bfa1 substrate (as monitored by Coomassie stain) added to the kinase reaction (bottom, MBP-Bfa1) are shown. The band that is shown for Kin4 associated kinase activity and total Bfa1 substrate is the first major degradation product of MBP-Bfa1 as described in Maekawa et al., 2007 and was the dominant signal.
(G) dyn1Δ (A17349), dyn1Δ kin4Δ (A17351), and dyn1Δ KIN4-S508A (A21301) were analyzed as in Figure 2C.