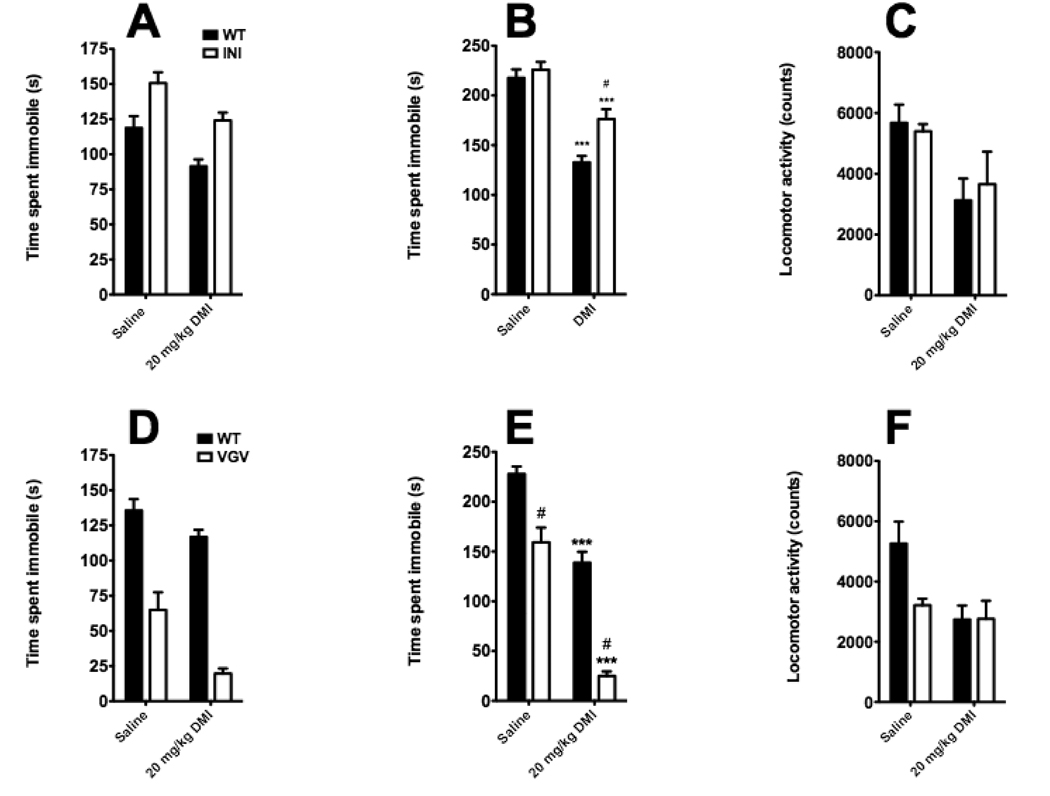
Figure 3. Impact of alterations of 5-HT2CR mRNA editing on despair behavior and antidepressant response in FST, TST and locomotor activity.
5-HT2CR-INI mice exhibit a pro-depressant phenotype in the FST (A) but not in the TST (B). Conversely, 5-HT2CR-VGV mice exhibit an antidepressant-like phenotype in both the FST (D) and TST (E). Both lines showed significant decreases in immobility in both tests in response to DMI (A, B, D, and E), and the effect of DMI was potentiated in 5-HT2CR-VGV in the TST but not the FST. DMI significantly decreased locomotor activity in both lines (C and F). There was no significant difference in locomotor activity in either line after vehicle injection (C and F), although there was a trend toward a decrease in the VGV mice (p = 0.09)(F). Values are means +/−SEM. * p < 0.05 and *** p < 0.001 for significant difference from respective saline-treated animals. # p < 0.05 for significant difference from respective wild-type animals. Full statistical analysis can be found in Table 1.