Figure 1.
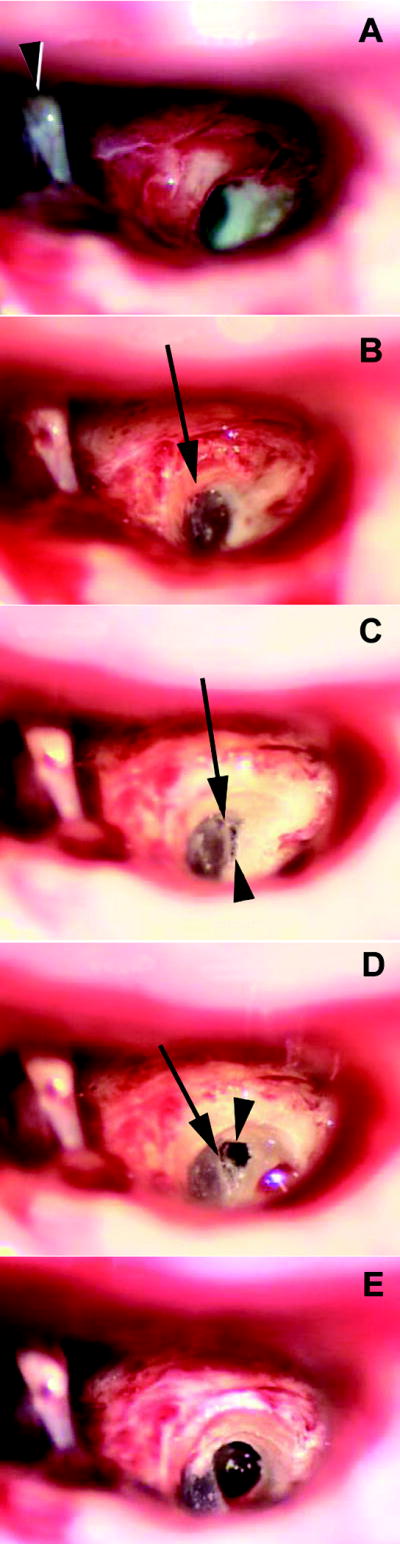
Technique of cochleostomy.
- A wide facial recess approach (right ear). The Fallopian canal is skeletonized and the bone medial to (underneath) the canal is removed to expose the tectulum (bony overhang) of the round window niche. (arrowhead: stapes)
- The tectulum is completely removed (arrow) exposing the entire round window.
- The bone inferior to the round window is thinned to expose the “endosteum” of the scala tympani (arrowhead). The bone removal is just inferior to the annulus (arrow) of the round window membrane.
- The thinned bone of the scala tympani is removed with rasps (arrowhead). Note that the cochleostomy is immediately adjacent to the inferior part of the round window (arrow).
- The completed cochleostomy. The size of the opening into the inferior most part of the scala tympani may vary depending on the size of the electrode array.
