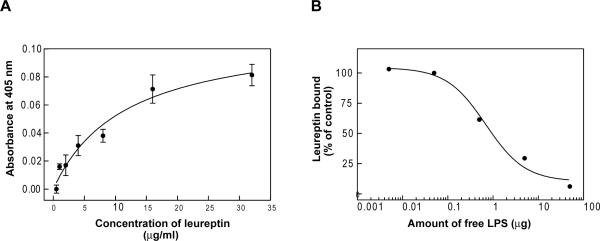
Fig. 6. LPS binding ability of leureptin.
(A) LPS binding assay. Purified leureptin isoform 1 from plasma was added in serial dilutions into an LPS-coated microtiter plate, and the binding assay was carried out as described in materials and methods. Each point represents the mean of three individual measurements ± SEM. The line represents the nonlinear regression calculation of one-site binding curve (R2 = 0.87). (B) Competition of free LPS for leureptin binding. Free LPS (0.005 – 50 μg) was added to each well of an LPS-coated microtiter plate simultaneously with 35μg/ml leureptin. The amount of the bound leureptin was measured as in materials and methods. The percentage of leureptin bound to immobilized LPS was calculated by comparison to the control, which contained no free LPS. The line represents the calculation of nonlinear regression of one-site competition curve (R2 = 0.99).