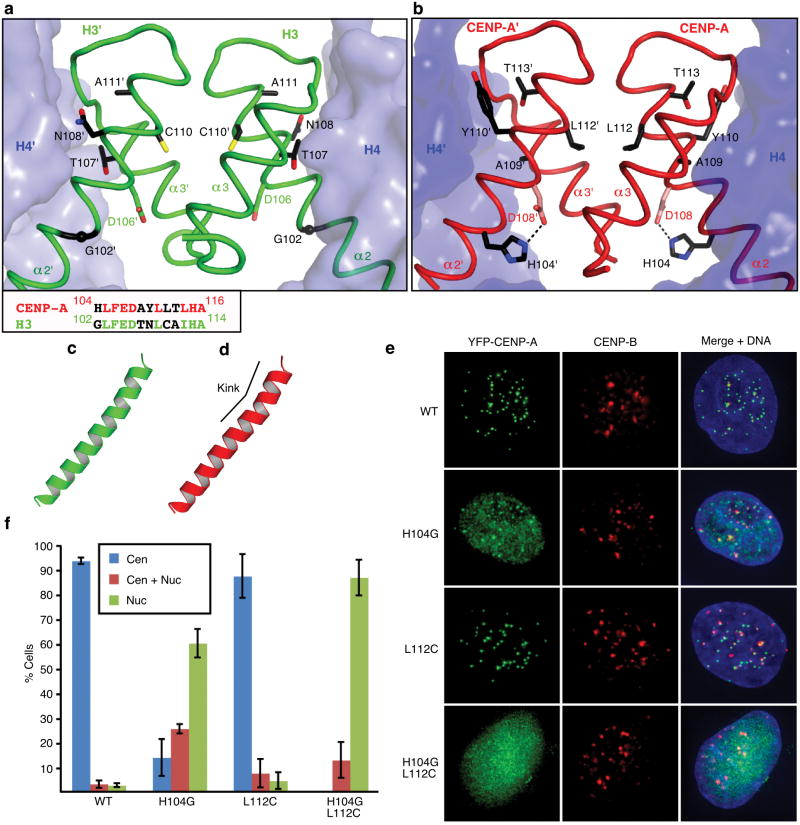
Figure 2. The residues involved in the rotated CENP-A/CENP-A interface are essential for centromere targeting.
Detail of H3/H3, a, and CENP-A/CENP-A, b, interfaces with side chains of 5 non-conserved residues in α2 helix at the interface. An alignment of residues in the C-terminal portion of the α2 helix are shown in the box at lower left in panel a. c and d, the α2 helices of H3, c, and CENP-A, d. e, Centromere targeting of WT and mutant versions of CENP-A. f, Quantitation of targeting experiment. For each version of CENP-A, 3 or more experiments were conducted in which a total of >250 cells were analyzed for localization (Cen = exclusively centromeric; Cen + Nuc = both centromere and nucleoplasm staining; Nuc = nucleoplasm only [i.e. no enrichment at centromeres]). Values are plotted +/- s.d.