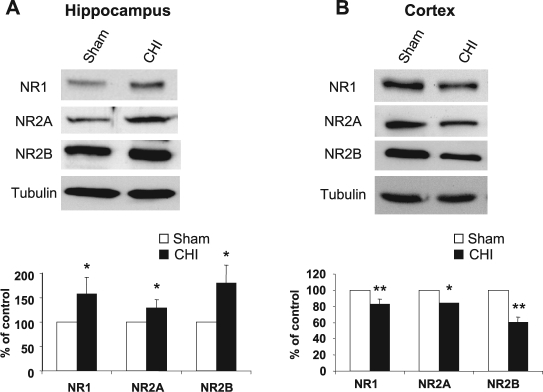
FIG. 2.
Closed head injury (CHI) induces an increase in the hippocampus and a decrease in cortical N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) subunits. (A) At 15 min following CHI, the hippocampus ipsilateral to the injured side was removed, homogenized, and total protein was isolated. Samples from sham and CHI mice (50 μg/lane) were resolved on 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Membranes were probed with anti-NR1, anti-NR2A, and anti-NR2B antibodies. Histogram depicts the level of proteins and presented as mean ± SD percent of (sham) control (n = 6 pools of 3 animals in each pool). **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05; significantly different from sham (Mann-Whitney test). (B) At 15 min following CHI, the cortex ipsilateral to the injured side was removed, homogenized and total protein were isolated and analyzed as in A. Histogram depicts the level of proteins presented as mean ± SD percent of (sham) control (n = 4 pools of 3 animals in each pool). **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05; significantly different from sham (Mann-Whitney test).