FIG. 4.
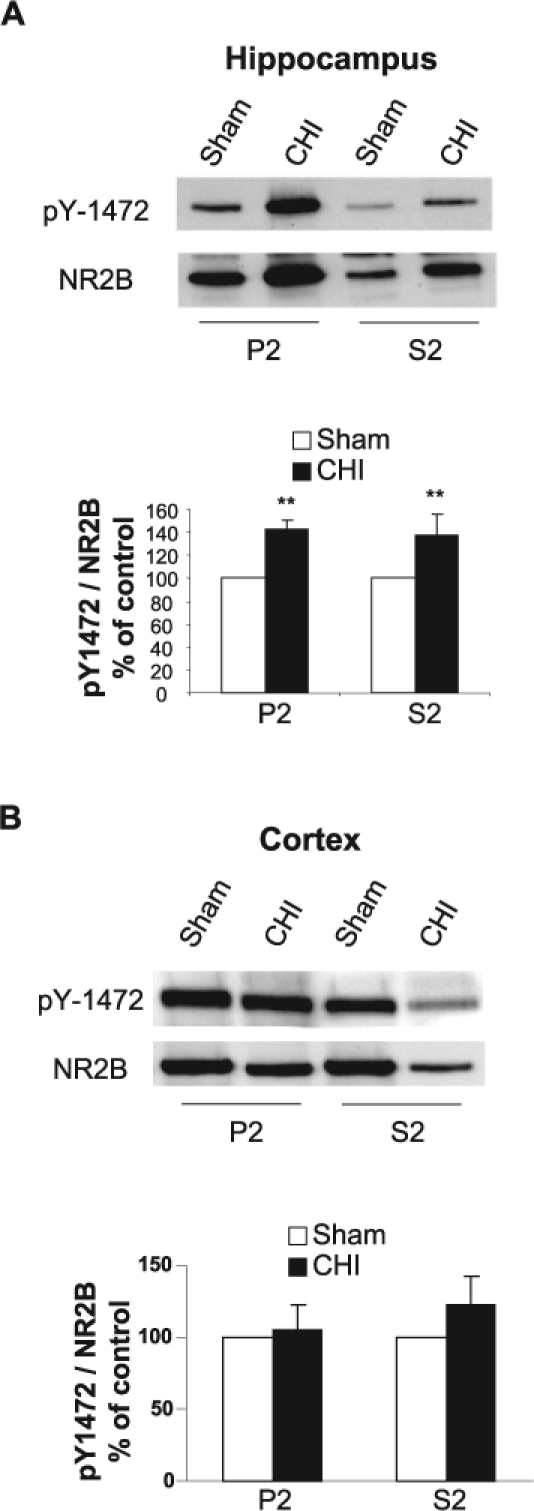
Closed head injury (CHI) induces an increase in tyrosine phosphorylation of the NR2B subunit in the hippocampus but not in the cortex. (A) At 15 min following CHI, the hippocampus ipsilateral to the injured side was removed, homogenized, and synaptosomal (P2) and light membranes (S2) fractions were isolated. Samples from sham and CHI mice (50 μg/lane) were resolved on 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Membranes were probed with anti-pY1472 and anti-NR2B antibodies, and the level of phosphorylation was normalized to NR2B. Representative blots are shown from sham (n = 4 pools of 3 animals in each pool) and CHI mice (n = 4 pools of 3 animals in each pool). Histogram depicts the level of NR2B pY-1472, presented as mean ± SD percent of (sham) control (n = 4 pools of 3 animals in each pool). **p < 0.01; significantly different from sham (Mann-Whitney test). (B) At 15 min following CHI, the cortex ipsilateral to the injured side was removed, homogenized, and total protein was isolated and analyzed as in A. Histogram depicts the level of NR2B pY-1472, presented as mean ± SD percent of (sham) control (n = 4 pools of 3 animals in each pool). No statistically significant difference in pY-1472 was detected between sham and CHI mice (Mann-Whitney test).
