FIG. 5.
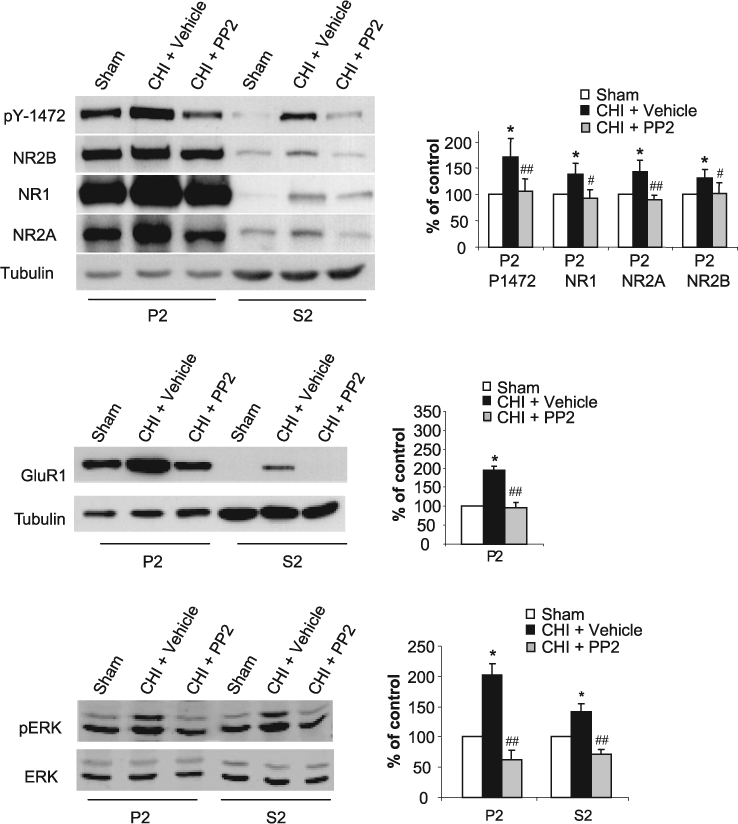
PP2 abolishes closed head injury (CHI)–induced increase in NR2B and ERK phosphorylation, and normalize the amount of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) and AMPA receptor (AMPAR) subunits in the hippocampus. Prior to the application of CHI, mice received i.p. injection of vehicle (CHI) or 0.03 mg/kg of PP2, the specific inhibitor of the Src-PTKs (CHI + PP2). After 15 min, the hippocampus ipsilateral to the injured side was removed, homogenized, and synaptosomal (P2) and light membranes (S2) fractions were isolated. Sham animals served as control (Sham). Samples (50 μg/lane) were resolved on 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Membranes were probed with anti-pY1472, anti-NR1, anti-NR2A, anti-NR2B (top); anti-GluR1 and anti-TfR (middle); anti-phospho-p44/42 MAPK and anti-p44/42 MAPK antibodies (bottom). Histograms depict the level of NR2B phosphorylation (normalized to total NR2B) and NMDAR subunits in the P2 fraction or GluR1 (normalized to tubulin) in the P2 fraction, and ERK phosphorylation (normalized to total ERK). Data are presented as mean ± SD percent of (sham) control (n = 6 pools of 3 animals in each pool). *p < 0.05, for sham vs. CHI+vehicle; or ##p < 0.01, #p < 0.05 for CHI+PP2 vs. CHI+vehicle (Mann-Whitney test).
