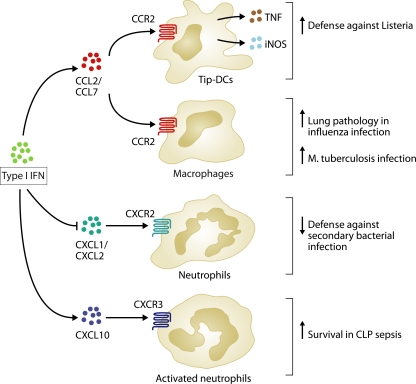
Figure 2.
Effects of type I IFN on chemokine production and leukocyte recruitment. Type I IFN drives the production of chemokines, such as CCL2 and CCL7, which recruits CCR2-expressing TNF and inducible nitric oxide synthase–producing DCs (Tip-DCs) that are required for defense against Listeria infection. CCR2-expressing macrophages also contribute to lung pathology during influenza infection and are highly permissive to infection with M. tuberculosis. During influenza infection, type I IFN inhibits the production of the CXCR2 ligands CXCL1 and CXCL2, thus decreasing neutrophil recruitment and dampening host defense against secondary bacterial infections. However, type I IFN also drives the production of CXCL10, which recruits activated CXCR3-expressing neutrophils, thus protecting against sepsis in response to CLP.