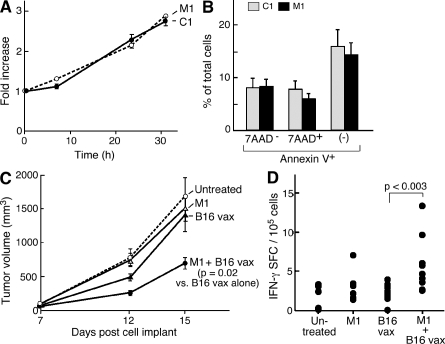
Figure 7.
IAP antagonists augment a prophylactic antitumor vaccine. (A) 104 B16 cells were plated in the presence of IAP antagonists or control compound. Fold increase was determined using CellTiter-Glo relative to time 0. (B) B16 cells were irradiated with 3.5 krad and cultured for 24 h in the presence of IAP antagonists or control compound. Apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry using annexin V and 7AAD staining. Results are representative of at least two independent experiments. (C) Tumor growth curves for C57BL/6 mice injected with 5 × 105 B16 melanoma cells on day 0. Mice either did not receive a vaccine or received vaccines comprising 150 mg/kg M1, 5 × 105 irradiated B16 cells, or 150 mg/kg M1 and irradiated B16 cells before tumor challenge. Eight mice were used per group. Data are consistent with two independent experiments using several distinct schedules and doses. (A–C) Error bars represent SEM. (D) On day 14, 2.5 × 105 CD8+ T cells were isolated from the spleens of mice vaccinated as indicated and stimulated by irradiated spleen cells pulsed with TRP-2 peptide or vehicle. IFN-γ–reactive cells were determined by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot.