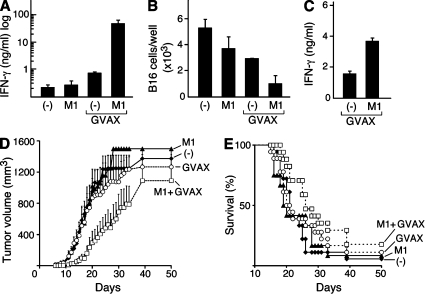
Figure 8.
IAP antagonists enhance immune responses to a therapeutic antitumor vaccine. (A–C) On day 0, mice were vaccinated with irradiated B16 cells engineered to secrete GM-CSF (GVAX) and were either left untreated or were given a 6-d course of 1,000 µg/day M1 by gastric lavage (GVAX M1). Untreated mice (−) and mice given M1 in the absence of GVAX (M1) were used as controls. (A and B) Vaccination site draining lymph nodes were harvested on day 7 and resuspended in 500 µl RPMI containing 10 U/ml recombinant human IL-2. Lymph node cells were incubated with 2 × 105 irradiated B16 cells for 4 d. (A) IFN-γ was measured in the culture supernatants by ELISA. (B) Total viable B16 cells were quantified by trypan blue exclusion. (C) 2 wk after vaccination, NK cells were isolated, activated, and analyzed as in Fig. 2 F. (A–C) Results are representative of at least two independent experiments with three to four mice per group. (D and E) On day 0, mice were challenged with 2 × 105 B16 cells. Mice were vaccinated as in A–C starting on day 1. Tumor growth (D) and survival (E) for mice after challenge are shown. Results represent the combination of three similarly designed, independent experiments with similar results for a total of 12–18 mice per group. (A–E) Error bars represent SEM.