Figure 2.
The Dwarf Phenotype of F4443 Is Caused by a Mutation in the SLR1 SAW Domain, Which Leads to a Reduced Interaction with GID1.
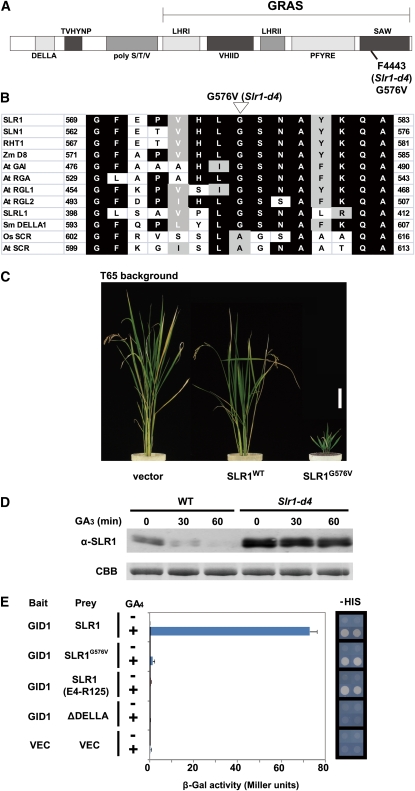
(A) Schematic structure of SLR1. The protein in F4443 (Slr1-d4) contains a G576V substitution (SLR1G576V).
(B) Comparison of the region around G576 of DELLA proteins from various plant species. Rice (Kamiya et al., 2003) and Arabidopsis (Di Laurenzio et al., 1996) SCR, which belong to another GRAS protein family, are also shown. Zm, Zea mays; At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Sm, Selaginella moellendorffii; Os, Oryza sativa.
(C) Gross morphology of transgenic plants at harvest. FLAG-tagged SLRWT and FLAG-tagged SLR1G576V were each overproduced in wild-type T65 rice. Vector, T65 transformed with proAct-FLAG/pCAMBIA control vector. Bar = 10 cm.
(D) Degradation of SLR1 and SLR1G576V protein upon GA3 treatment in rice callus. Nipponbare and Slr1-d4 calli were incubated with 10−5 M GA3 for the indicated times, and the crude protein extracts were subject to immunoblot analysis using an anti-SLR1 antibody. The loading control of Coomassie blue (CBB) staining is shown in the bottom panel.
(E) Interaction between GID1 and SLR1G576V with (+) or without (−) 10−4 M GA4. Left, β-Gal activity detected in a liquid assay with yeast strain Y187 transformants (means ± sd; n = 3). Right, Growth of yeast strain AH109 transformants on –HIS plates. GID1 was used as bait, and SLR1 and its mutants were used as prey. SLR1 (E4-R125), DELLA/TVHYNP domain; ΔDELLA, SLR1 containing a deletion in the DELLA domain (from D39 to A55).