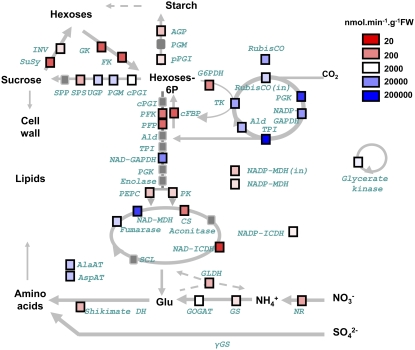
Figure 1.
Assignment of Enzymes to Pathways and Average Maximum Enzyme Activities across All the Accessions.
Rubisco and NADP-GAPDH are specific for the Calvin-Benson cycle, AGP for starch synthesis, cFBP and SPS for sucrose synthesis, PFK, PFP, NADH-GAPDH, PK, and PEPC for glycolysis, G6PDH for the oxidative pentose phosphate (OPP), and INV, SuSy, FK, and GK for sucrose breakdown and the use of hexose sugars. TPI, Ald, and PGK are involved in the Calvin-Benson cycle and glycolysis and TK in the Calvin-Benson cycle and the OPP pathway. TPI, Ald, PGK, and TK are assigned to the Calvin-Benson cycle because the major isoforms of these enzymes are located in the chloroplast stroma (Heldt, 1997) and because fluxes are 10- to 100-fold higher in photosynthesis than in glycolysis (Geiger and Servaites, 1994; Gibon et al., 2004a). UGP is involved in the synthesis and breakdown of sucrose, and PGI and PGM are involved in the synthesis and breakdown of sucrose and starch. The assays distinguished plastidic PGI (pPGI) and cytosolic (cPGI) (Gibon et al., 2004b). UGP was assigned to sucrose synthesis. Several TCA cycle enzymes have additional functions. CS and NAD- and NADP-ICDH are required to generate 2-oxoglutarate, which is the C-acceptor during nitrate and ammonium assimilation. NADH-MDH is involved in the synthesis of malate and, together with NADP-MDH, in metabolite cycles that allow redox equivalents to be exchanged between the NADP system in the plastid and the NAD systems in the cytosol and the mitochondrion (Scheibe, 2004). The maximum catalytic activities of each enzyme, averaged across all accessions, are shown by color coding (see figure for scale). All abbreviations are defined in Supplemental Data Set 1C online. The subscript “in” for Rubisco and NADP-MDH indicates “initial activity.”