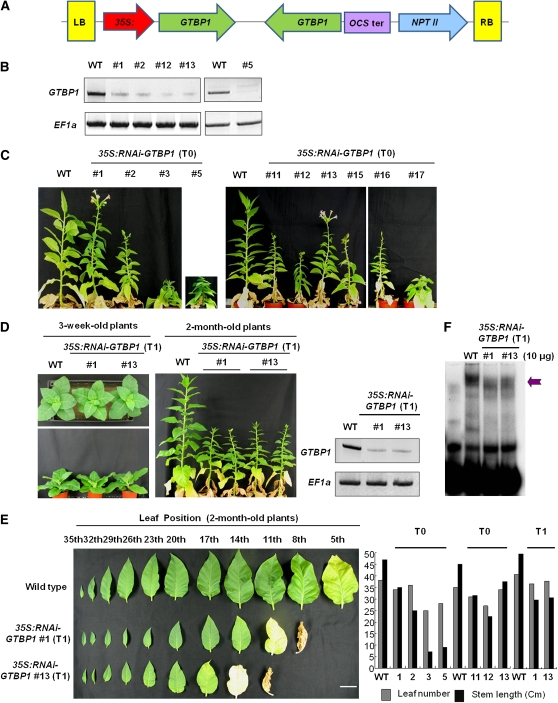
Figure 4.
Construction and Characterization of 35S:RNAi-GTBP1 Knockdown Transgenic Tobacco Plants.
(A) Schematic structure of GTBP1 RNAi binary vector construct. The 35S:RNAi-GTBP1 vector includes the inverted-repeat sequence of the N-terminal (122 to 498 bp) or C-terminal (726 to 1070 bp) regions of GTBP1 cDNA. LB, left border; OCS ter, octopine synthase terminator; NPTII, neomycin phosphotransferase II; RB, right border.
(B) Repression of GTBP1 mRNA in transgenic plants. Total leaf RNA from wild-type and independent T0 35S:RNAi-GTBP1 lines was analyzed by RT-PCR. EF1α was used as a loading control.
(C) Gross morphology of 2-month-old wild-type and independent T0 transgenic lines grown under greenhouse conditions.
(D) Morphology of 3-week-old and 2-month-old wild-type and T1 RNAi transgenic lines (#1 and #13). GTBP1 transcript levels were determined by RT-PCR in T1 generation (shown at the right with EF1α as a control).
(E) Morphological comparison of leaves from 2-month-old wild-type and T1 transgenic (#1 and #13) plants. Leaf number and stem length of wild-type and 35S:RNAi-GTBP1 (T0 and T1) tobacco plants are shown in the right panel. Bar = 3 cm.
(F) Single-strand telomere binding activities of wild-type and T1 RNAi transgenic seedlings. The cell-free nuclear extracts containing 10 μg of protein were prepared from wild-type and T1 transgenic seedlings (#1 and #13), incubated with PT4, and analyzed by gel retardation assays as described in Figure 2. Arrow indicates protein-PT4 complex.
[See online article for color version of this figure.]