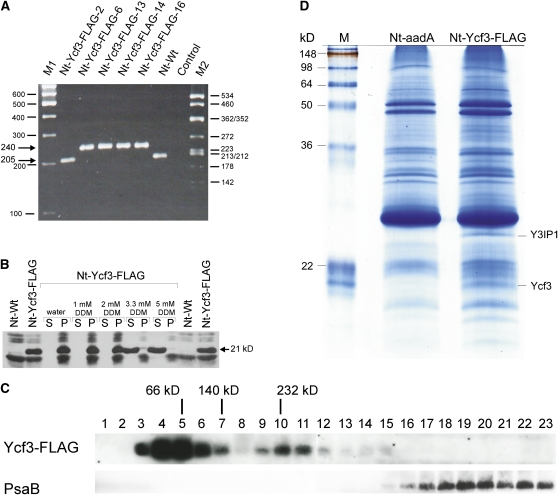
Figure 2.
Molecular Analysis of Nt-Ycf3-FLAG Plants.
(A) Homoplasmy of plastid transformants expressing a FLAG-tagged version of the ycf3 gene. PCR amplification with primer pair P5′/P3′ (Figure 1B) yields a 205-bp product for the wild type and a 240-bp product for the transplastome. Absence of the 205-bp fragment from lines Nt-Ycf3-FLAG-6, 13, 14, and 16 suggests homoplasmy for the FLAG-tagged ycf3 gene. Line Nt-Ycf3-FLAG-2 is transplastomic but carries only the aadA and not the FLAG mutation due to homologous recombination between the FLAG sequence and the aadA insertion site (Figure 1; Bock et al., 1994; Hager et al., 2002). This line was subsequently used as control (and referred to as Nt-aadA; see [C]). Homoplasmy for the aadA selectable marker gene was additionally confirmed by genetic crosses and inheritance assays. M1, M2, molecular mass markers (sizes of bands indicated in base pairs); control, buffer control.
(B) Association of the Ycf3 protein with thylakoid membranes. In Nt-Ycf3-FLAG plants but not in the wild type (Nt-Wt), the monoclonal anti-FLAG antibody recognizes a protein of 21 kD, which corresponds to the theoretical molecular mass of FLAG-tagged Ycf3. DDM treatment of purified thylakoids releases the protein from the membranes at concentrations of 3.3 mM and above (S, supernatant; P, thylakoid pellet). Cross-reacting bands present in thylakoid preparations from both the wild-type and the transplastomic plant are likely to represent LHC proteins. Note that they remain membrane bound at both 3.3 and 5 mM DDM, as expected for integral membrane proteins.
(C) Identification of Ycf3 complexes by sucrose gradient centrifugation. Sucrose gradients were fractionated into 23 fractions (numbered from top to bottom) and, following electrophoretic separation, probed with the anti-FLAG antibody to identify Ycf3-containing fractions (top panel) or with an anti-PsaB antibody to identify PSI-containing fractions (bottom panel). Peaks of relevant marker proteins from the molecular mass marker gradient are indicated above the blots.
(D) Detection of a putative interaction partner of Ycf3. Eluates from immunoprecipitation experiments with Nt-Ycf3-FLAG plants and Nt-aadA control plants were separated in a 15% polyacrylamide gel and stained with colloidal Coomassie blue. In addition to the band representing the FLAG-tagged Ycf3, another band, labeled Y3IP1, was specifically and reproducibly detected only in the Nt-Ycf3-FLAG samples, qualifying this protein as a potential interaction partner of Ycf3. M, molecular mass marker.