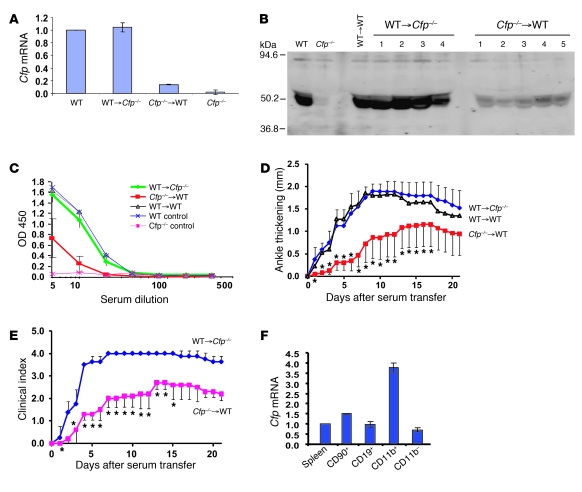
Figure 2. BM-derived cells are the major source of pathogenic properdin in K/BxN arthritis.
(A) Real-time PCR analysis of Cfp mRNA levels in BM cells of chimeric mice. Gapdh was used as an internal control, and values were normalized to those of WT mice. (B) Western blot analysis of properdin in the plasma (2 μl/lane) of chimeric mice. Numbers refer to individual mice. WT and Cfp–/– mouse plasmas were used as controls. Rabbit anti-mouse properdin serum was used as the primary Ab. (C) ELISA plate assay of LPS-induced AP complement activity in sera of chimeric mice. (D) K/BxN serum-induced arthritis in chimeric mice, as assessed by changes in ankle thickness (relative to day 0). *P < 0.05 versus WT→Cfp–/–, nonparametric Wilcoxon/Kruskal-Wallis test. (E) K/BxN serum-induced arthritis in chimeric mice, as assessed by clinical score. *P < 0.05 versus WT→Cfp–/–, nonparametric Wilcoxon/Kruskal-Wallis test. (F) Real-time PCR analysis of Cfp mRNA levels in splenic T (CD90+) and B (CD19+) lymphocytes and granulocytes/macrophages (CD11b+). All 3 types of cells were positively selected from splenocytes (pooled from 8 WT mice) by column purification. CD11b– cells were the leftover fraction from CD11b+ selection. Gapdh was used as an internal control, and values were normalized to that of total splenocytes (Spleen). Values represent mean ± SD of triplicate PCR assays.